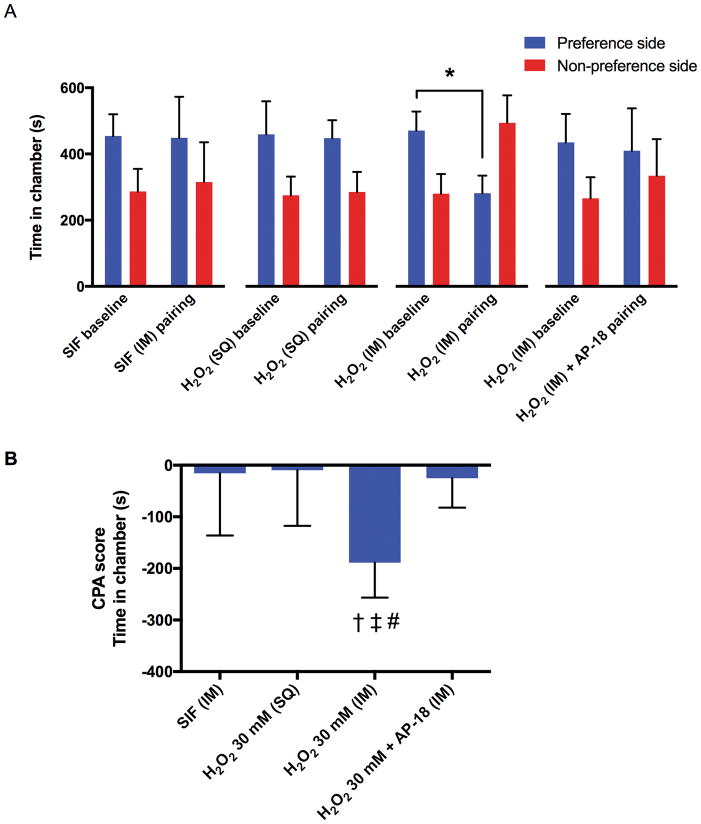
Fig. 3. Effects of intramuscular (IM) or subcutaneous (SQ) injection of 30 mM H2O2 on conditioned place aversion (CPA) in rats.
Each column represents the time spent in the preferred and non-preferred chambers during the pre- and post-conditioning sessions (A), and the CPA scores (B) of the intramuscular injection of SIF group (n = 8), subcutaneous injections of H2O2 (30 mM, 0.6 ml) group (n = 8), and intramuscular injection of H2O2 (30 mM, 0.6 ml) group (n = 8), intramuscular sequential-injection of AP-18 (50 mM, 0.3 ml) followed by H2O2 (60 mM, 0.3 ml) group (n = 9). All data are expressed as means ± SD. * P = 0.0011 by paired t-test. † = 0.0036 compared with the SIF group, ‡ P = 0.0026 compared with the subcutaneous injection of H2O2 group, # P = 0.0048 compared with the intramuscular co-injection of H2O2 and AP-18 group by one-way ANOVA (F3, 29 = 7.212, P = 0.0009) followed by post-hoc Tukey’s test.