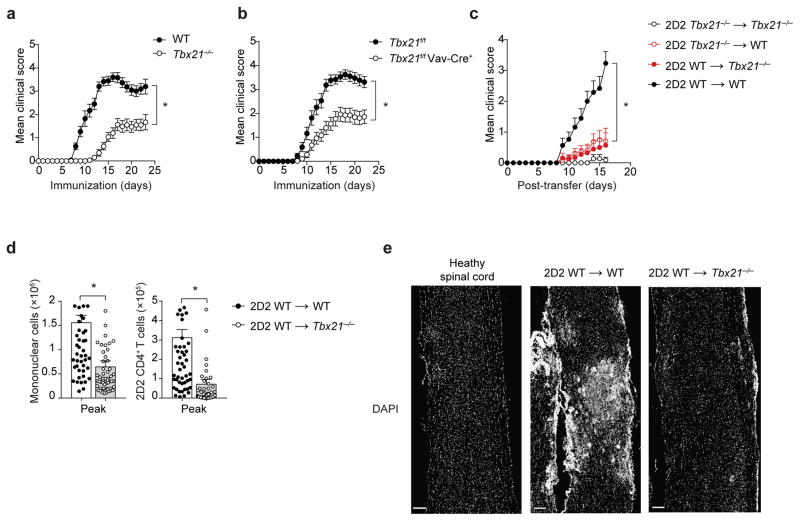
Figure 1.
T-bet expression in T cells is insufficient to cause EAE. (a–b) Mean clinical scores in wild-type (WT) versus Tbx21−/− mice (a), or Tbx21f/f versus Tbx21f/f Vav-Cre+ mice (b), immunized with MOG35-55/CFA and pertussis toxin. (c) Mean clinical scores in Tbx21−/− or WT mice receiving 5 × 106 2D2 Tbx21−/− or 2D2 WT TH17 cells. (d) Enumeration of total CNS-infiltrating mononuclear cells or CNS-infiltrating 2D2 CD4+ T cells (CD4+Vβ11+) at the peak of EAE disease (day 15–17 post-transfer), in Tbx21−/− or WT recipients of 2D2 WT TH17 cells (5–7.5 × 106), analyzed by flow cytometry. (e) DAPI staining of spinal cord longitudinal sections from a naïve healthy mouse or Tbx21−/− or WT recipients of 2D2 WT TH17 cells (7.5 × 106). Scale bar, 200 μm. *, P < 0.0001 (two-way ANOVA (a–c) or two-tailed Student’s t-test (d)). Data are combined from three independent experiments (a; mean ± s.e.m. of n = 30 mice per group), four independent experiments (b; mean ± s.e.m. of n = 28 mice per group), five independent experiments (c; mean ± s.e.m. of n = 15 – 20 mice per group) and 12 independent experiments (d; mean ± s.e.m. of n = 54, 57 mice per group). Histological images are representative of three independent experiments (n = 6, 9 mice per group).