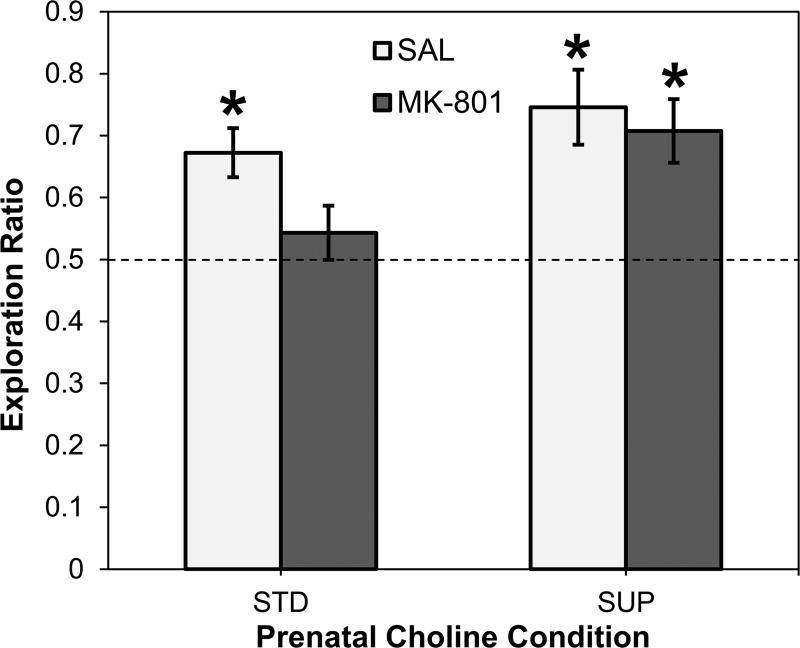
Figure 1.
Object recognition memory using the novelty preference task as a function of prenatal dietary condition and low dose MK-801 or saline administration. Average exploration ratios for each of the four groups are shown as reflection of the extent to which rats displayed biases toward the novel object during the test phase of the task. The dashed line reflects no bias for either object. *p < 0.05 versus no bias value of 0.50.