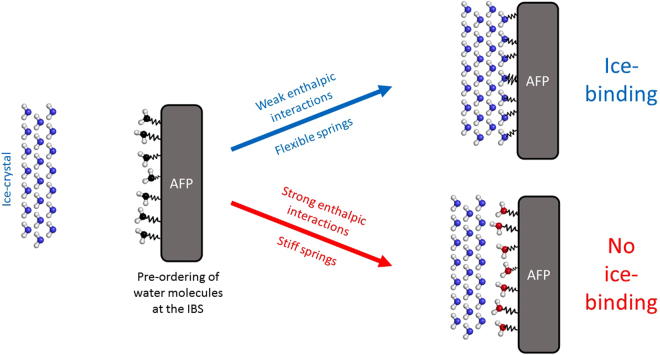
Figure 5.
Schematic representation of the ice-binding process highlighting the influence of enthalpic interactions between the protein and the first hydration shell. Pre-ordering of the water molecules in an ice-like structure around the IBS (left); if the protein water interactions are too strong, the water molecules cannot rearrange and an energetically unfavorable mismatch between the ice and the protein occurs (bottom right). If the enthalpic interactions are weak, the springs are flexible and the water molecules are able to rearrange and fit to the ice lattice (top right).