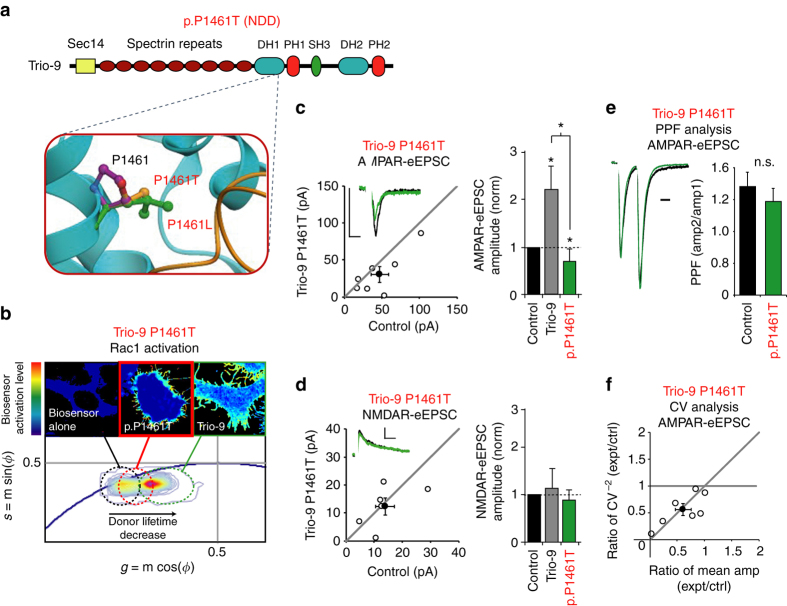
Fig. 6.
Trio-9 p.P1461T expression reduces the strength of glutamatergic synapses. a Predicted alteration to Trio’s GEF1 domain resulting from Trio-9 P1461T. NDD, neurodevelopmental disorder. b Trio-9 P1461T inhibits Trio-9’s ability to activate Rac1. Representative FLIM color maps of HEK293 cells expressing the Rac1 biosensor alone, the biosensor and Trio-9 P1461T or the biosensor and Trio-9 are shown above. A cropped phasor plot for each condition is shown below. Dashed ovals identify the lifetime distribution for each condition. Complete phasor plots are shown in Supplementary Fig. 2. c, d Scatterplots show eEPSC amplitudes for single pairs of control and transfected neurons (open circles). Filled circles show mean ± SEM. (Insets) Current traces from control (black) and transfected (green) neurons (Scale bars: 20 ms for AMPA, 50 ms for NMDA, 20 pA). Bar graphs show the average eEPSC amplitudes (±SEM) of neurons expressing Trio-9 (in gray, from Fig. 4j, k) and Trio-9 P1461T normalized to their respective average control eEPSC amplitudes. In the bar graphs a Wilcoxon Rank Sum Test was used to compare across independent conditions (i.e., Trio-9 and Trio-9 P1461T in c, *P < 0.05). c Trio-9 P1461T expression reduced AMPAR-eEPSC amplitude (n = 7 pairs, *P < 0.05, Wilcoxon Signed Rank Test). d Trio-9 P1461T expression did not affect NMDAR-eEPSC amplitude (n = 6 pairs, P > 0.05, Wilcoxon Signed Rank Test). e Mean ± SEM paired-pulse facilitation (PPF) ratios for Trio-9 P1461T expressing and paired control neurons (n = 5 pairs, P > 0.05, Student’s t-test). Peak 1-scaled current traces from control (black) and transfected (green) neurons (Scale bar: 20 ms). n.s., not significant. f CV analysis of AMPAR-eEPSCs from pairs of control/Trio-9 P1461T neurons. CV−2 graphed against ratio of mean amplitude within each pair (open circles). Filled circle shows mean ± SEM. (n = 7 pairs)