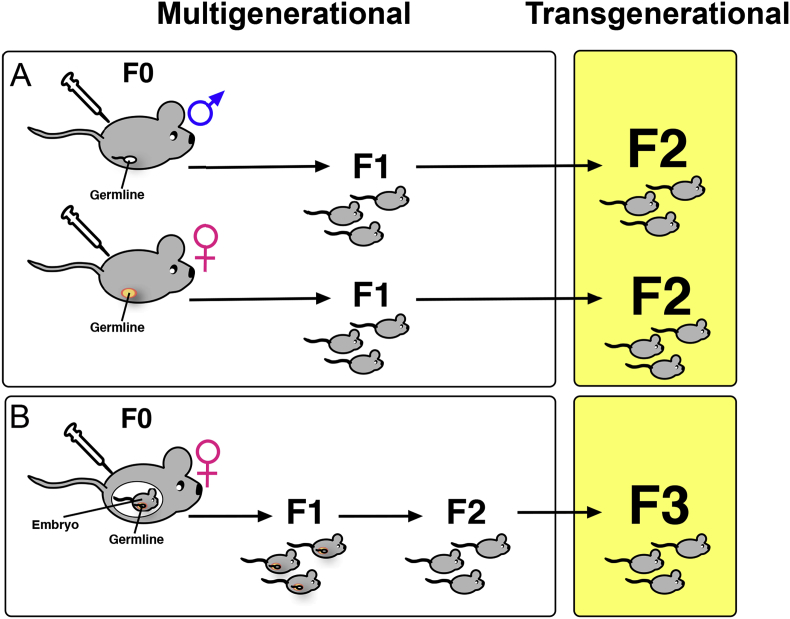
Figure 3.
Epigenetic inheritance can be multigenerational or transgenerational. A) Multigenerational inheritance refers to a change in a trait or phenotype in the F1 offspring of males or non-pregnant females (F0) exposed to a stimulus that impacts the epigenome without changing the DNA sequence. B) In the case of a pregnant female exposed to an environmental toxin, for instance, the F0 parent, the F1 fetus, and the F2 germline within the fetus are all exposed. Therefore, in this case, only if the F3 generation also shows an epigenetically altered phenotype does transgenerational inheritance occur.