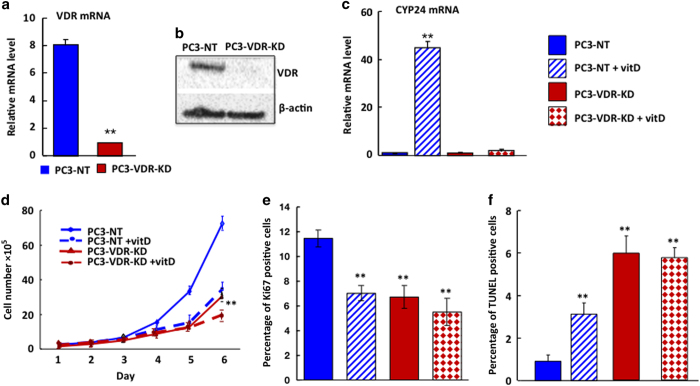
Figure 3.
Effects of VDR knockdown in prostate cancer (PC3) cells—in vitro studies. (a,b) Compared to non-target controls (PC3-NT, cells transfected with non-target RNA), VDR mRNA (A) and protein (B) expression was knocked down by 80% in PC3-VDR-KD cells at 24 h post plating. **P< 0.001. (c) Treatment of PC3-NT and PC3-VDR-KD cells with 10−8 mol·L−1 1,25(OH)2D3 for 8 h increased CYP24 expression by more than 40-fold in NT cells with no appreciable response in knockdown cells. **P<0.001 compared to baseline. (d-f): Culture of PC3-NT and PC3-VDR-KD cells under ligand-free conditions. Compared to NT cells, cell growth (d) and cell proliferation (Ki67 immunoreactivity, (e) of MDA-VDR-KD cells were reduced by 49% and 41%, respectively, while apoptosis was increased to six fold (f). Treatment of PC3-NT cells with 10−8 mol·L−1 1,25(OH)2D3 reduced cell growth by 51% (d) and Ki67 positivity by 38% (e) while inducing a 3-fold increase in apoptosis (f) compared to untreated PC3-NT cells. In contrast, the same treatment had no effect on the growth or apoptosis rates of PC3-VDR-KD cells (d–f). *P<0.05; **P<0.01 compared to respective controls. In vitro experiments were performed in triplicate and repeated at least three times. Results shown are from a single representative experiment. Data are expressed as mean±s.e.m. (n=3).