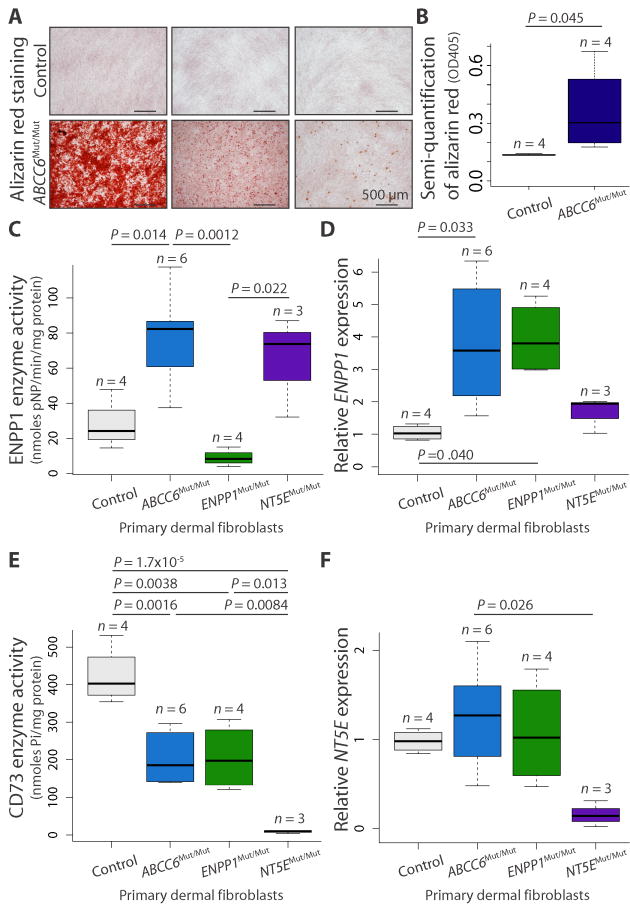
Fig. 2.
Evidence for a provoked cell-autonomous defect and alterations in enzymes integral to the extracellular catabolism of ATP in ABCC6 mutant cells.
(A) Primary dermal fibroblasts derived from patients with biallelic mutations in ABCC6 (ABCC6Mut/Mut) calcify in vitro when stimulated with osteogenic media, as indicated by alizarin red staining. Representative images demonstrating the spectrum of calcification are shown. (B) Quantification of the alizarin red staining was determined by colorimetric analysis. One-tailed Student’s t test was performed (P = 0.045). (C to F) Quantification of enzyme activity and gene expression for ENPP1 (ENPP1) and CD73 (NT5E) in primary dermal fibroblasts derived from patients with biallelic mutations in ABCC6, ENPP1, or NT5E. A one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s honest significance difference post hoc analysis was performed. One-way ANOVA: (C) P = 0.001; (D) P = 0.016; (E) P = 3.51 × 10−5; (F) P = 0.038. P values of post hoc comparisons are indicated in the figure.