Extended Data Figure 1. Mass-spectrometric analysis of HP1α proteins. Cross-linking Mass Spectrometry of HP1α identifies extensive interactions between the Chromoshadow domain(CSD) and the hinge region.
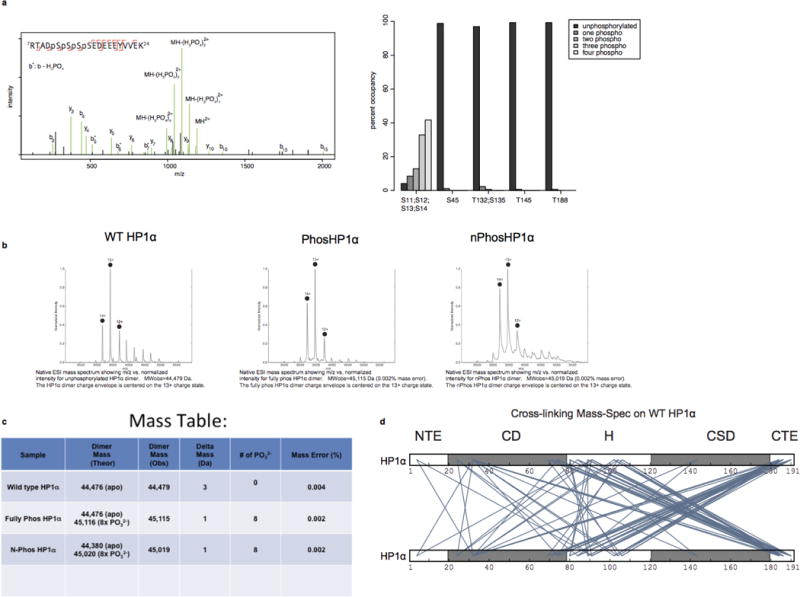
a, Phosphorylation of HP1α occurs almost exclusively at the N-terminus. Left panel: Annotated HCD product ion spectra of a quadruply phosphorylated, doubly charged HP1α peptide at Ser11, Ser12, Ser13, Ser14. Neutral loss of phosphoric acid from b-ions is indicated by b*. Right panel: Relative occupancy of observed HP1α phosphorylation sites as estimated by spectral counting. 41.7% of product ion spectra from peptides containing Serines 11–14 were observed quadruply phosphorylated (393 of 943 spectra). An additional 32.9% (310 spectra), 12.8% (121 spectra), and 8.5% (80 spectra) were identified triply, doubly, and singly phosphorylated, respectively, while only 4.1% (39 spectra) were observed with no phosphorylation. In contrast, phosphorylation was observed at other positions (Ser45, Thr132 and/or Ser135, Thr145, and Thr 188) with 1–2.5% occupancy (1059, 2243, 1586, 1042 total spectra observed for peptides containing these residues). b, Native MS charge state envelopes for WT, Phos- and nPhos- HP1α. c, Table with predicted and observed masses is also shown. The deconvoluted masses fit best to dimeric HP1α modified by 8-phosphates in Phos-HP1α and nPhos-HP1α samples. d, Cross-links were identified by separating cross-linked HP1α by SDS-PAGE and excising bands corresponding to monomeric and dimeric HP1α. Putative inter protein cross-links, diagrammed here, were identified by taking the set of cross-links that are unique to the dimer band (from three replicates). Only cross-links identified by 4 or more product ion spectra are shown for clarity.
