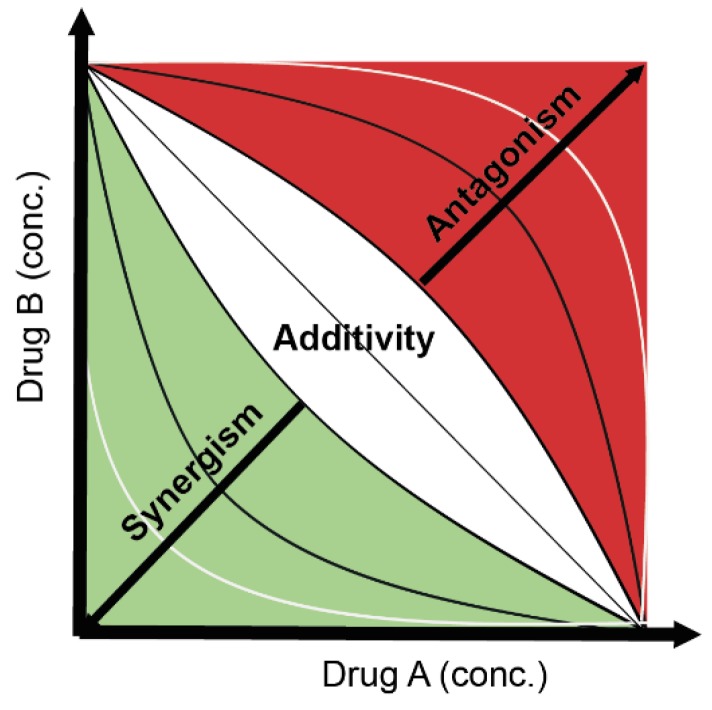
Figure 1.
Schematic isobologram showing the equi-effective Cartesian plane for the combination of Drug A and Drug B at a specific effect level fa (for example fa = 0.5). For any mixture ratio (A:B), the effect of A + B should be theoretically located on the straight transversal line (the additivity line). The additivity effect can consider uncertainty (depicted by the white region). When the doses of A + B required to get the desired effect (fa) is less than that expected from their theoretical fractional summation of their respective individual effects (see Equation (4)), the effect of A + B is synergistic, and their coordinate location in the isobologram Cartesian plane is below the additivity line, depicting synergism. The opposite case indicates antagonism. Figure adapted from Cokol et al. [25]. Copyright 2011, EMBO and Macmillan Publishers Limited.