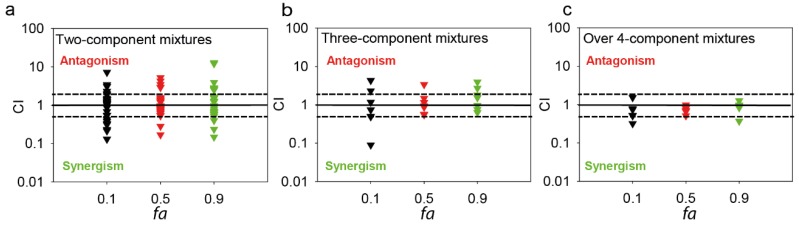
Figure 4.
CI values of two-component mixtures (n = 63) (a); three-component mixtures (n = 21) (b) over four-component mixtures (n = 18), (c) at three representative effect levels fa (0.1, 0.5, 0.9 ) for a variety of pollutant combinations, such as heavy metals, herbicides, perfluorinated surfactants, and pharmaceuticals, elaborated based on the data published in Rodea-Palomares et al. [33,34,51], Rosal et al. [35] and Gonzalez-Pleiter et al. [38]. CI axis in logarithmic scale. Straight lines represent additivity, broken lines indicate suggested limits for significant departures from additivity (CI = 2 as upper limit for antagonism, CI = 0.5 as upper limit for synergism).