Figure 2.
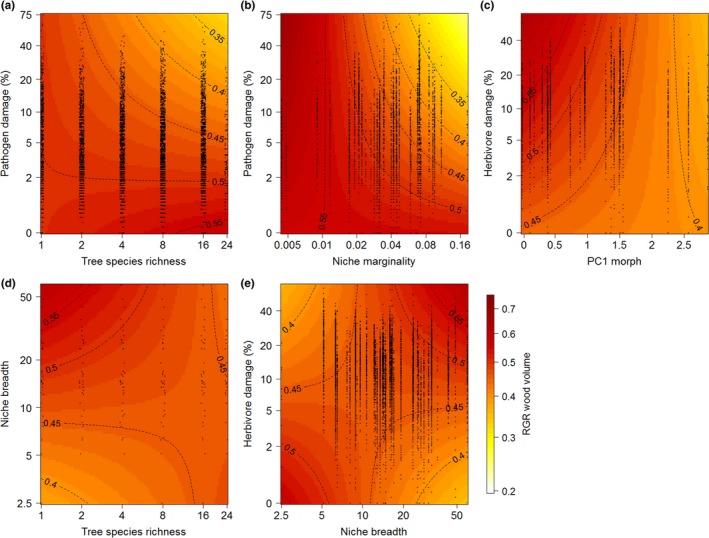
Interactive effects of tree species richness, plant traits, insect herbivores, and fungal pathogens on the relative growth rates (based on wood volume) of the trees planted in the “BEF‐China” tree diversity experiment. Colors and isolines show predicted values of the mixed‐effects model of relative growth rates. All interactions were significant at p ≤ .05 (see Table 3). Black circles show the distribution of observations (jittered for better visualization)
