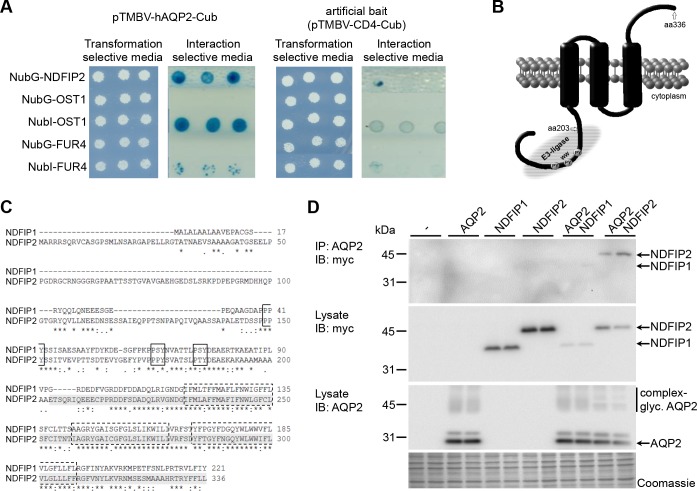
Fig 2. NDFIP2, a NEDD4 family interacting protein, binds to AQP2 in a MYTH assay.
(A) Specific interaction of NDFIP2 with AQP2. Colony growth on interaction-selection media of yeast cells expressing NubG-NDFIP2 together with AQP2 indicates interaction (left two panels). No colony growth is detected with the artificial bait (CD4-Cub) a human integral membrane protein (right two panels). NubG-OST and NubI-OST serve as negative and positive controls for interaction in the ER-membrane, respectively, whereas NubG-FUR4 and NubI-FUR4 serve as negative and positive controls for interaction in the plasma membrane, respectively. These data confirm expression of AQP2 in the ER and plasma membrane of yeast cells and reveal the absence of self-activation. (B) Topology and interaction elements of NDFIP2. The part of NDFIP2 found to interact with AQP2 (amino acid 203–336, indicated with grey marking) covers part of the N-tail, the transmembrane domains (indicated with dashed line) and a part of the luminal/extracellular C-terminus. The PY elements which interact with the NEDD4/4L ww domains are indicated with a closed line. (C) Alignment of the sequences of human NDFIP2 and NDFIP1. Of the sequence of NDFIP2 (isoform 1; NP_061953.2) found to interact with AQP2 in the MYTH assay (aa 203–336, grey), 68% is identical (*) and 86% is similar (. or:) to that of NDFIP1 (NP_085048.1). The PPY-motifs (black rectangle) known to bind to NEDD4 and NEDD4L are not, but the transmembrane domains (dashed rectangle) are within the AQP2 binding region. (D) NDFIP1 and NDFIP2 interact with AQP2. HEK cells were transiently-transfected with an empty construct (-), or constructs encoding myc-tagged NDFIP1, NDFIP2 or AQP2 separately or combined (indicated on top), grown for 2 days, lysed and subjected to AQP2-immunoprecipitation (IP: α-AQP2). The IP-fractions (upper panel) and total lysates (indicated) were immunoblotted for NDFIP1 or -2 (IB: α-myc), or AQP2 (IB: α-AQP2). Only when co-expressed with AQP2, NDFIP1 and NDFIP2 were detected in the immunoprecipitate. Coomassie staining of the blots confirmed loading of protein equivalents. Molecular masses of proteins are indicated on the left (in kDa).