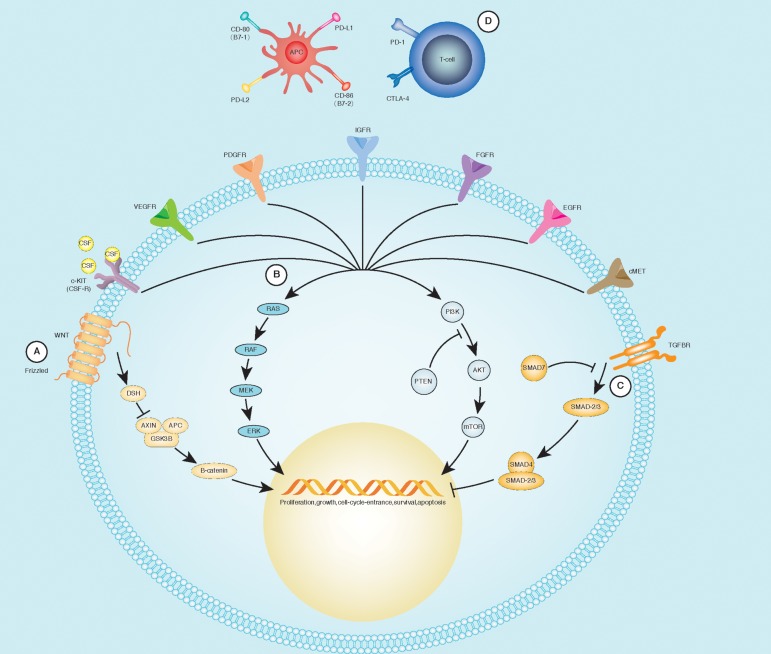
Fig. 1. Main molecular pathways in HCC pathogenesis.
(A) The activation of Frizzled (WNT receptor) determines the recruitment of disheveled (DSH), preventing the destruction of β-catenin through the dissolution of a molecular complex composed by Axin, adenomatosis polyposis coli (APC), and glycogen synthase kinase 3β (GDK3B). (B) Growth factors bind their specific receptors, leading to their dimerization and activation of the tyrosine-kinase. From this point, it is possible to recruit two different groups of molecules: MAPK and PI3K pathways, culminating with modifications in cell-cycle regulation, protein synthesis, and gene transcription. (C) Stimulation of TGF-βR recruits the SMAD complex, leading to a negative regulation of the cellular cycle. (D) CTLA-4 and its ligands: CD-80/CD-86 transmit an inhibitory signal in the antigen presenting cells (APCs), while CD-28 represents an activating signal. Programmed cell death protein-1 (PD-1), through its binding to PD-L1 (B7-1) and PD-L2 (B7-2), down-regulates the immune system and promotes self-tolerance. Adapted from Harding et al.121