Fig. 4.
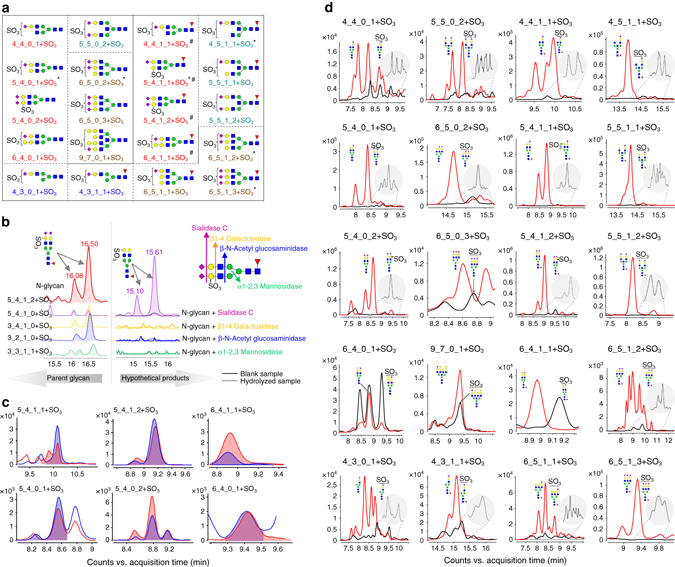
Structures of sulfated N-glycans identified on human serum IgGs. a Structures of identified sulfated N-glycans in human serum IgG. (*represents sulfated N-glycans that have been reported from a human source; #represents sulfated N-glycans that have been reported on porcine thyroglobulin; another 11 sulfated N-glycans have not been previously reported). b Four exoglycosidases, Sialidase C, β1–4 galactosidase, β-N-acetyl glucosaminidase, and α1–2, 3 mannosidase, were employed to hydrolyze the sulfated N-glycans to determine site of the sulfate group. c The retention times and peak patterns of sulfated N-glycans in human IgGs (red) were compared with those in porcine thyroglobulin (blue), which has been well characterized. d The retention time of each sulfated N-glycan (black) is 0.5 min later than its corresponding parent N-glycans (red), and the signal intensity is 3-fold to 200-fold lower than that of the non-sulfated N-glycans
