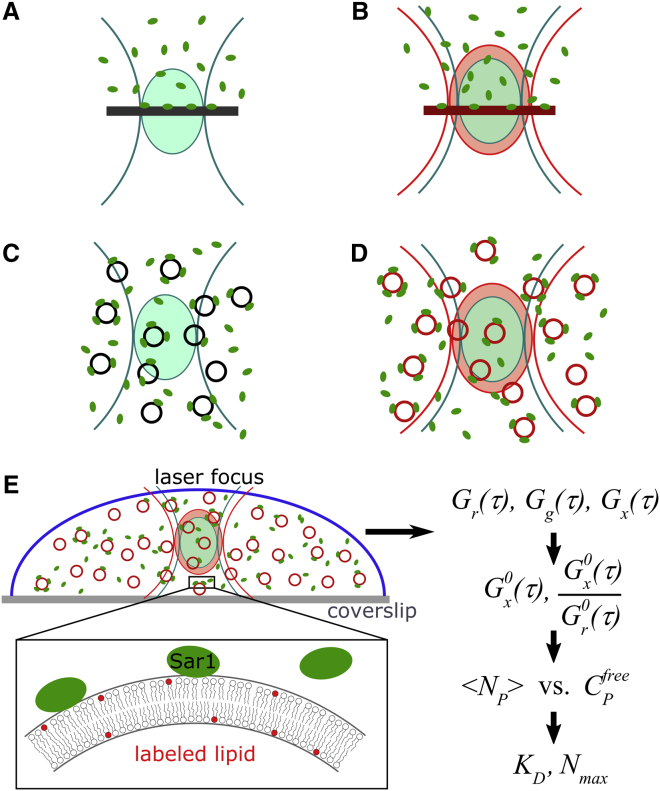
Figure 1.
FCS/dcFCCS configurations for analyzing ligand-membrane binding. (A) Autocorrelation analysis of a labeled ligand binding to an unlabeled planar membrane. Fractions of bound and free ligand are quantitated by a two-component diffusion model. Measured fractions are sensitive to focus position. (B) Same geometry as in (A), with additional exploitation of a distinctly labeled binding partner in the membrane and dual-color cross-correlation. (C) Analysis of freely diffusing ligand-liposome particles. The ligand is labeled; free and liposome-bound fractions are quantitated by a two-component diffusion model. The influence of binding stoichiometry needs to be considered or liposomes used in large excess (8, 9, 10). (D) Same geometry as in (C), with additional exploitation of distinctly labeled liposomes. (E) Implementation of configuration (D) in this work. The dcFCCS foci are placed on the binding reaction, which occurs in an aqueous buffer. The liposome bilayer is labeled with a red-fluorescent lipid analog. Green fluorescently labeled Sar1p protein constitutes the ligand that binds to the liposomes. Using the cross-correlation and red autocorrelation amplitudes, the degree of ligand binding versus free ligand is obtained. A Langmuir isotherm model is applied, yielding the number of total binding sites and the dissociation constant. To see this figure in color, go online.