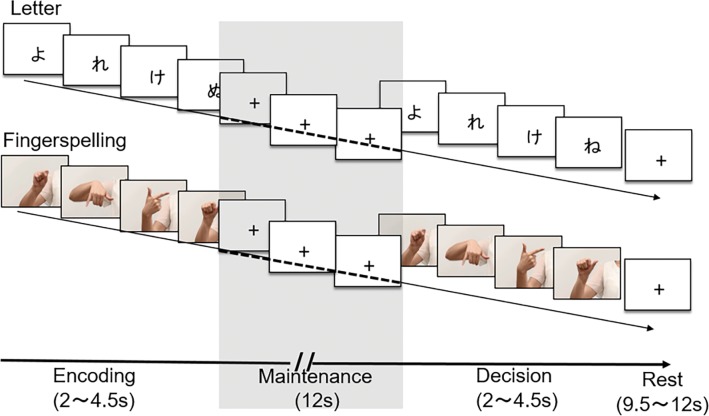
Fig 1. Experimental design of the sequence memory span task.
On each trial, a nonsense sequence of 4–7 syllables was presented either as letters (Japanese kana) or as fingerspelling. Participants were instructed to read and memorize the first syllable sequence during encoding stage and keep the syllable sequence for 12 seconds during maintenance stage (highlighted). They then viewed another syllable sequence and decided by key-press whether or not two sequences were identical during the decision phase.