Fig. 1.
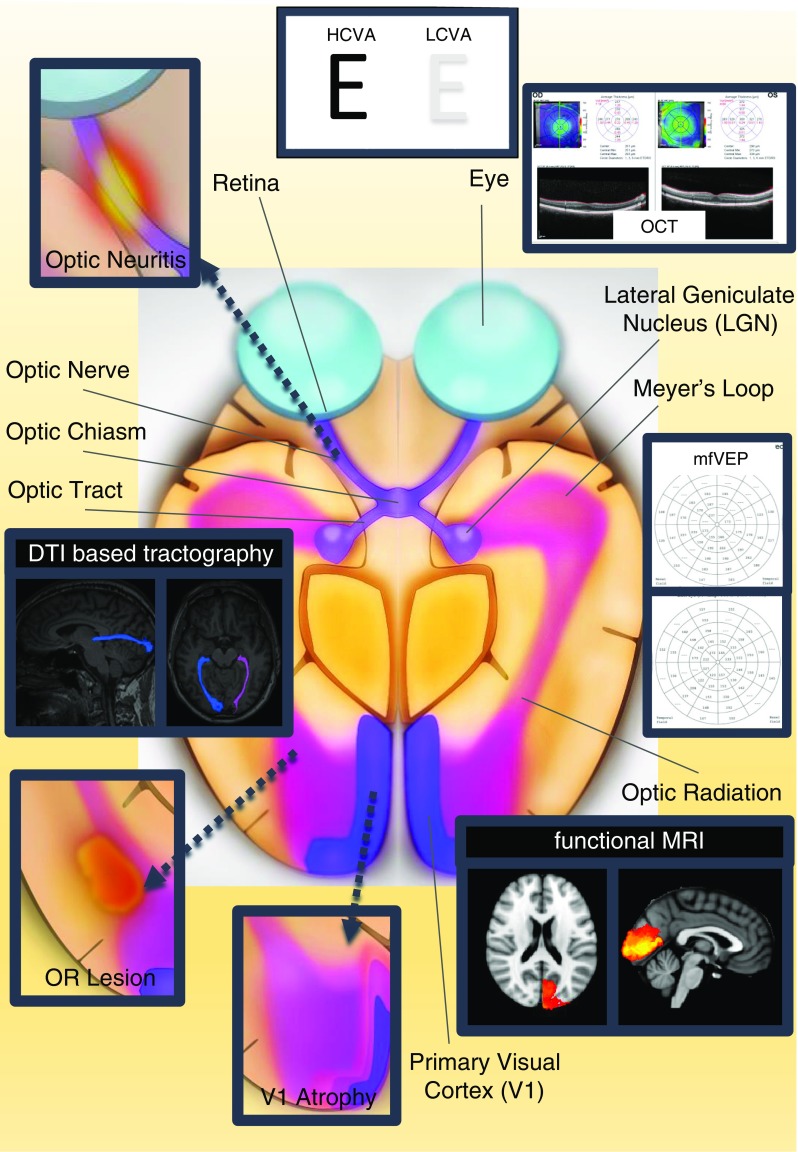
Selection of visual pathway anatomical structures and assessment methods. Important anatomical structures are displayed: retina, optic nerve, optic chiasm, and optic tract are parts of the anterior visual pathway and lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN), optic radiation, and primary visual cortex are parts of the posterior visual pathway. Optic neuritis within the optic nerve, OR lesions within the optic radiation, and V1 atrophy of the visual cortex are displayed as typical damage patterns in neuroinflammatory diseases, e.g., multiple sclerosis. Whereas HCVA and LCVA may assess the overall functionality of the visual system, other methods provide information on different visual system parts, i.e., OCT of the retina, DTI-based tractography of the optic radiation and functional MRI of the visual cortex. MfVEP evaluates latency delays along the entire pathway from optic nerve to V1 area. This figure was made by use of InkScape (https://inkscape.org/en/). OR lesion optic radiation lesion, V1 atrophy primary visual cortex atrophy, DTI diffusion tensor imaging, OCT optical coherence tomography, mfVEP multifocal visual evoked potentials, HCVA high-contrast visual acuity, LCVA low-contrast visual acuity, LGN lateral geniculate nucleus
