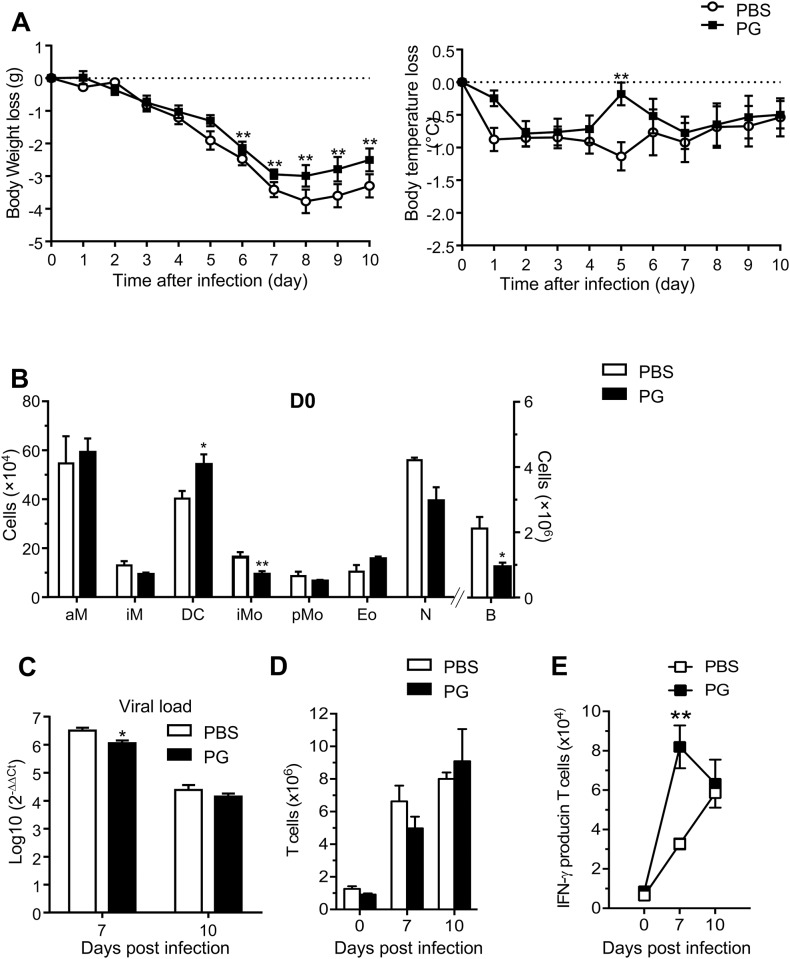
Fig 6. Effect of L. paracasei derived-peptidoglycans on influenza_infected mice.
(A) Effects of consumption of PG of L. paracasei by mice (n = 17 at D0) on body weight loss and temperature loss compared with PBS control group (n = 17 at D0). (B) Effect of consumption of PG of L. paracasei (n = 10) on the recruitment of immune cells in the lungs at day 0 compared with the control group (n = 10): aM: Alveolar Macrophage, iM: Interstitial Macrophage, DC: Dendritic cells, iM: Inflammatory Monocyte, pM: Patrolling monocytes, Eo: Eosinophils, N: Neutrophils, B: B cells, T: T cells. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM for each group. (C) Effect of consumption of PG of L. paracasei (n = 17 at D0) on viral load in IAV-infected BALB/c mice compared with the control group (n = 17 at D0), 7 and 10 days after viral infection. Data are means ± SEM of each group of mice (*p<0.05).