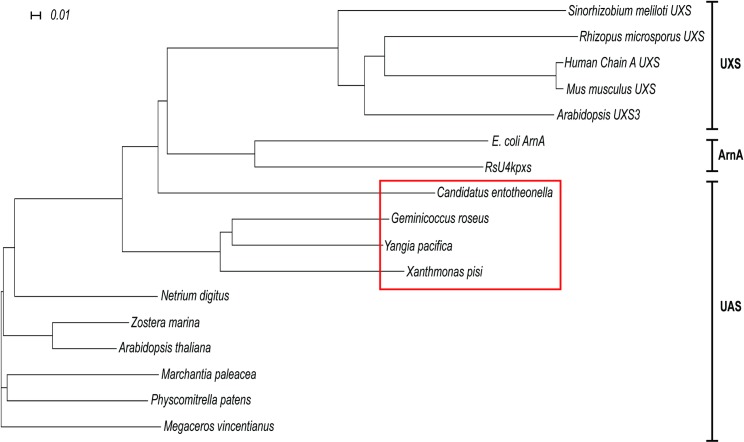
Fig 2. Phylogeny of bUASs.
Phylogenetic analysis of proteins involved in the synthesis of UDP-apiose (UAS) and UDP-xylose (UXS). Amino acid sequences used are the C-terminal region of Escherichia coli ArnA (WP_032205568.1) that forms UDP-4-keto-arabinose, Ralstonia solanacearum UDP-4-keto-pentose/UDP-xylose synthase (RsU4kpxs, WP_011001268.1), UXSs from bacteria (Sinorhizobium meliloti, ACY30251.1) mammal (human & Mus musculus, NP_079352.2 & NP_080706.1), fungi (Rhizopus microsporus, CEI96046.1) and plant (Arabidopsis UXS3; NP_001078768.1). The bacterial UAS-like sequences used are from Candidatus entotheonella, Geminicoccus roseus, Xanthomonas pisi and Yangia pacifica (ETX00953.1, WP_084506503.1, WP_084725965.1 and WP_066111466.1). Other UASs used are from green algae (Netrium digitus, AOG75413.1), from hornwort (Megaceros vincentianus, AOG75412.1), from liverwort (Marchantia paleacea, AOG75410.1) from moss (Physcomitrella patens, AOG75414.1), and from angiosperms (Arabidopsis thaliana & Zostera marina, KMZ68719.1 & NP_180353.1). Bacterial UAS are outlined by a red box. Alignment was made using Clustal Omega [24–26] and the tree generated using Dendroscope [20].