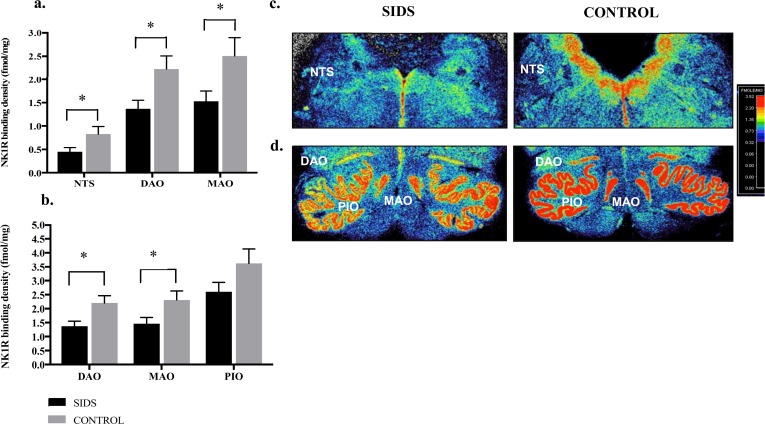
Fig 3. Consistent significant absolute reductions in NK1R binding (fmol/mg) in SIDS cases compared to non-SIDS controls.
a. NK1R binding SIDS vs. acute controls. Compared to acute controls, NK1R binding was significantly reduced in SIDS cases in the NTS (p = 0.04), DAO (p = 0.01) and MAO (p = 0.03), b. NK1R binding in SIDS vs. combined controls. NK1R binding was significantly reduced in SIDS cases in the DAO (p = 0.01) and MAO (p = 0.03) with borderline significance in the PIO (p = 0.09) when compared to all controls combined (acute, chronic and hypoxic).c. Autoradiograms displaying NK1R binding (fmol/mg) in the NTS nuclei. Absolute reductions in NK1R binding were consistently observed in SIDS cases. d. Autoradiograms displaying NK1R binding (fmol/mg) in component nuclei of the IO. NK1R binding was consistently reduced in SIDS cases. *p = <0.05, **p = <0.01.