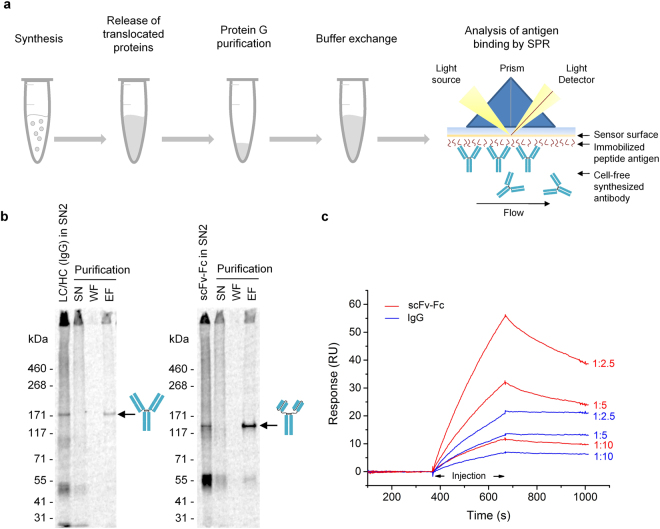
Figure 5.
Analysis of CECF-produced IgG and scFv-Fc by surface plasmon resonance (SPR). (a) Scheme depicting the established work flow prior to SPR analysis. Sample preparation included cell-free synthesis of IgG and scFv-Fc in CECF reactions, release of translocated proteins from the lumen of microsomal vesicles, Protein G purification as well as desalting and buffer exchange, followed by subsequent SPR measurement of samples. (b) Autoradiograph derived from SDS-PAGE gel demonstrating purification of IgG (left) and scFv-Fc (right) from supernatant fraction 2 after detergent solubilization (SN2) using Protein G coupled magnetic beads. SN: bead supernatant, WF: washing fraction, EF: elution fraction. (c) Biacore sensorgrams showing the specific binding of purified scFv-Fc and IgG to immobilized peptide antigen SMAD2P. Samples were diluted 1:10, 1:5 and 1:2.5 to show concentration-dependent binding. Protein yields were assessed by the analysis of identically treated samples synthesized in the presence of 14C-leucine. Dilutions of 1:10, 1:5 and 1:2.5 correspond to protein concentrations of approximately 0.07 µg/mL, 0.15 µg/mL, 0.3 µg/mL containing Protein G purified IgG and 0.09 µg/mL, 0.18 µg/mL, 0.37 µg/mL containing Protein G purified scFv-Fc. Sensorgrams are double reference subtracted (CXCR5 as non-related peptide antigen, HC as analyte). LC: antibody light chain; HC: antibody heavy chain; scFv-Fc: single-chain variable fragment Fc fusion.