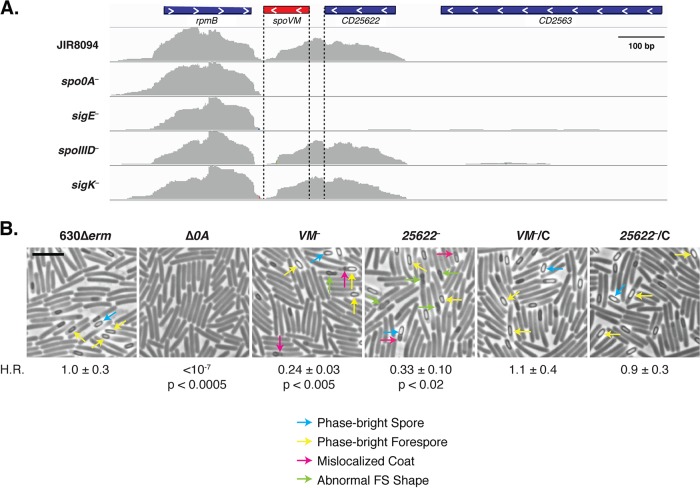
FIG 2 .
The CD25622-VM locus is largely dispensable for heat-resistant spore formation. (A) RNA-Seq transcript data of the CD25622-VM locus in wild-type JIR8094 and spo0A, sigE, spoIIID, and sigK mutant TargeTron insertion strains (36) visualized using the Integrative Genomics Viewer software (65). spo0A encodes the master transcriptional regulator necessary for induction of sporulation. sigE encodes σE, a mother cell-specific sigma factor that activates spoIIID transcription (59, 66, 67). spoIIID encodes a transcription factor that coordinately activates sigK transcription along with σE (36, 67). The proximity of C. difficile VM to rpmB, which encodes a ribosomal subunit protein, is conserved relative to other VM-carrying organisms (7). CD25622 appears to be unique to the Peptostreptococcaceae (41). The angled brackets indicate the direction of transcription. (B) Phase-contrast microscopy of wild-type 630Δerm, Δ0A, and VM mutant and CD25622-TargeTron mutants and their complements (VM::ermB/C and 25622::ermB/C) sporulating cultures at 20 h. Examples of phase-bright forespores and spores are marked using yellow and blue arrows, respectively. Select forespores with abnormal morphologies are delineated by green arrows, while regions that may correspond to mislocalized coat are highlighted in pink. H.R. refers to the heat resistance of each strain relative to the wild type. The means and standard deviations shown are based on four biological replicates. Statistical significance relative to the wild type was determined using a one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s test. Bars, 5 µm.