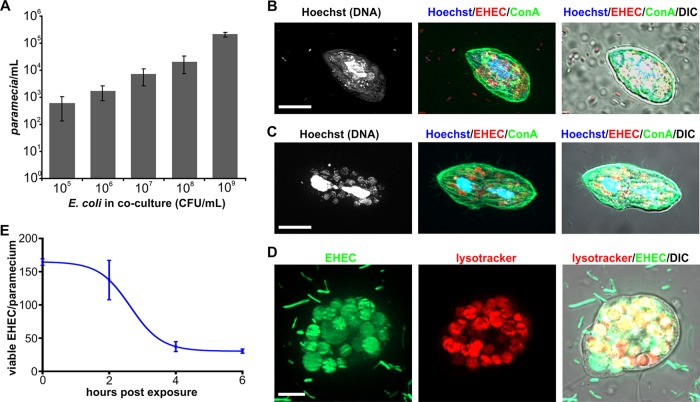
FIG 1 .
Paramecium caudatum acts as a vector for Escherichia coli. (A) EHEC and P. caudatum were grown in coculture for 16 h, and P. caudatum numbers were measured using a hemocytometer. Numbers of paramecia at the end of the experiment were graphed against initial bacterial concentrations (in CFU per milliliter). Values shown are means ± standard deviations (SD) (n = 3). (B) Following 2 h of coincubation with EHEC::mCherry (red), P. caudatum samples were fixed and subjected to Hoechst staining (DNA, blue) and concanavalin A (ConA) staining (green). (C) Some paramecia were proliferating on a diet of EHEC and were undergoing cell division. Scale bars, 10 μm. (D) Following 2 h of coculture with EHEC::gfp (green), P. caudatum was incubated with lysotracker (red) to visualize vacuole acidification. Scale bar, 5 μm. (E) Following 2 h of coincubation with EHEC, P. caudatum was transferred to medium without bacteria. Samples were removed at the indicated time points, and numbers of viable E. coli cells within paramecia were determined by dilution plating on selective agar (n = 3).