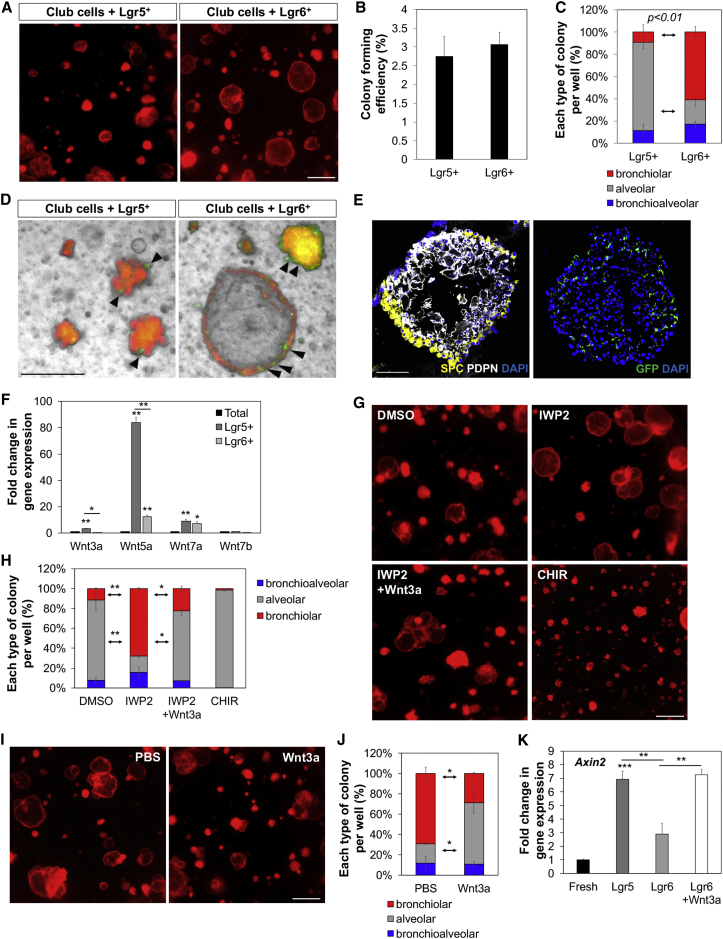
Figure 7.
Distinct Role of Lgr5 and Lgr6 in Regulating Lineage Differentiation of Lineage-Labeled Scgb1a1+ Cells
(A–D) Representative merged images of fluorescence (A) and phase contrast (D), colony forming efficiency (B), and quantification of each distinct type of primary lung organoids (C) from Scgb1a1+ cells co-cultured with Lgr5+ or Lgr6+ cells at 14 days in co-cultures. Arrowhead indicates close interactions of Lgr5+ or Lgr6+ cells (GFP, green) to club cell organoids (TdTomato, red).
(E) Representative IF images of alveolar organoids from Scgb1a1+/Lgr5+ co-cultures. (Left) SPC (yellow), PDPN (white), and DAPI (blue) are shown. (Right) GFP (for Lgr5, green) and DAPI (blue) are shown.
(F) qPCR analysis for expression of Wnt ligands in isolated total lung (black bar), Lgr5+ (dark gray bar), and Lgr6+ (light gray bar) cells. Shown is normalized to Gapdh.
(G) Representative fluorescent images of Scgb1a1+/Lgr5+ co-cultures with addition of DMSO, IWP2, IWP2 and Wnt3a, and CHIR.
(H) Quantification of each distinct type of colony from (G).
(I) Representative fluorescent images of Scgb1a1+/Lgr6+ co-cultures with addition of PBS and Wnt3a.
(J) Quantification of each distinct type of colony from (I).
(K) qPCR analysis for expression of Axin2 in freshly isolated Scgb1a1+ cells (black bar) and in Scgb1a1+ organoids co-cultured with Lgr5+ (dark gray bar), Lgr6+ (light gray bar), and Lgr6+ cells with Wnt3a treatment (white bar). Shown is normalized to Gapdh.
Data presented are the mean of three independent experiments with triplicates (B, C, H, J, and K) or with three individual mice (F). Error bars indicate SD (∗p < 0.01; ∗∗p < 0.005; ∗∗∗p < 0.001). The scale bars represent 500 μm (A, G, and I) and 100 μm (D and E). See also Figure S6.