FIG 1.
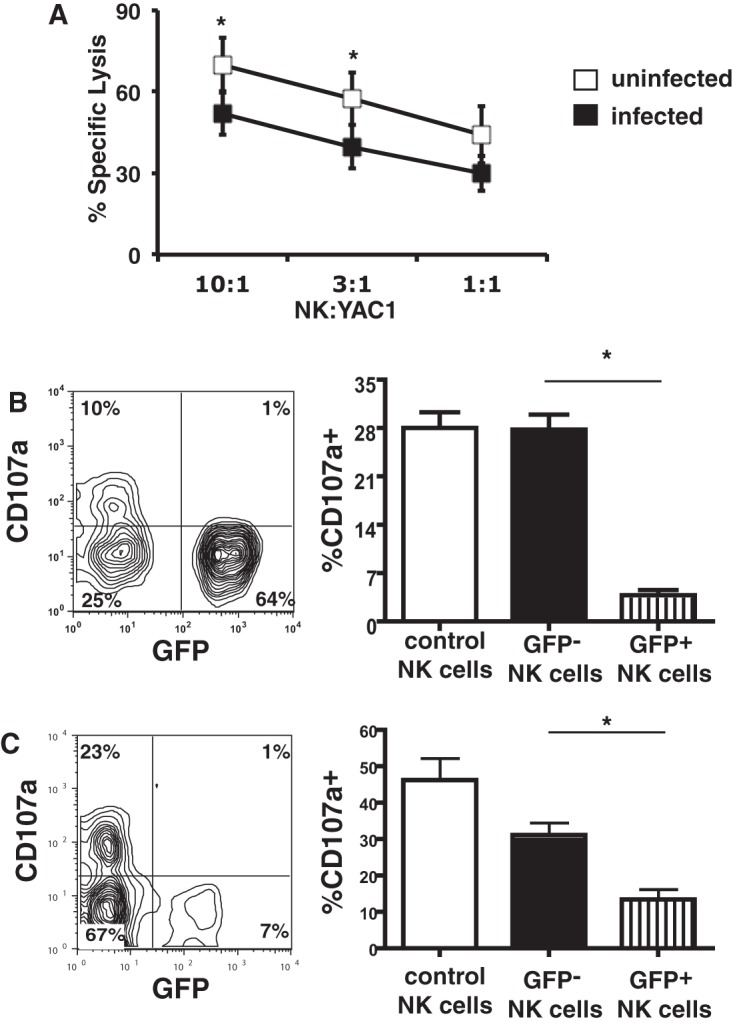
Infection of NK cells with T. gondii inhibits NK cell-mediated killing. (A) YAC1 cell killing by uninfected IL-2-stimulated NK cells or by NK cells infected with the RH-LDM T. gondii strain in the 51Cr release assay. The data represent means ± SEMs. *, P < 0.05, paired t test (n = 3 separate experiments). (B) Degranulation by IL-2-stimulated NK cells. (Left) Results of one representative experiment of degranulation by NK cells in the presence of YAC1 cells (10:1); (right) bar graph representing the percentage of CD107a+ cells by gating on the infected (GFP+) or uninfected (GFP−) NK cells separately. *, P < 0.01, ANOVA with the Bonferroni correction (n = 6 separate experiments). Control NK cells represent NK cells not exposed to T. gondii in culture. (C) Degranulation by NK cells following NK1.1 cross-linking. (Left) Results of one representative experiment; (right) bar graph representing the percentage of CD107a+ by gating on the infected (GFP+) or uninfected (GFP−) NK cells separately from all experiments. *, P < 0.01, ANOVA with the Bonferroni correction (n = 5 separate experiments). Control NK cells represent cells not exposed to T. gondii in culture.
