Figure 1.
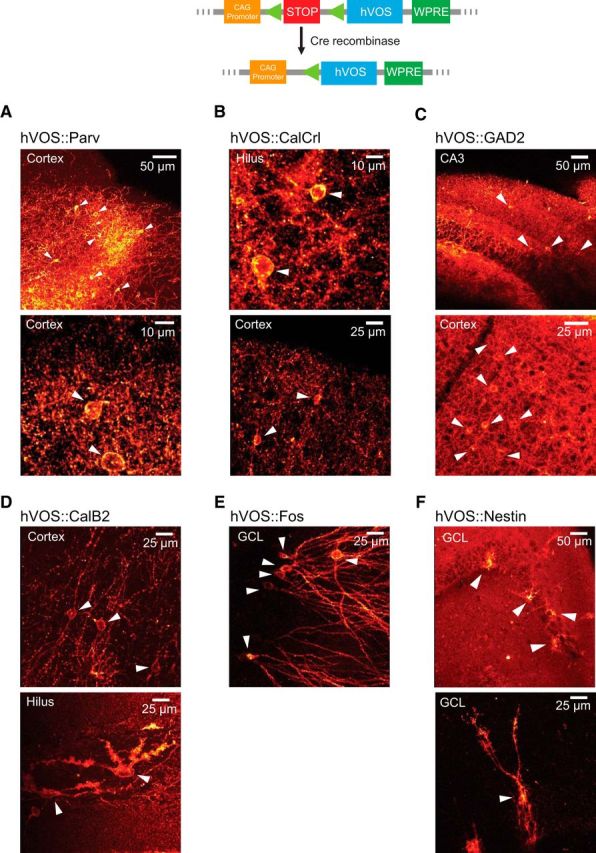
hVOS probe expression in Cre-targeted neurons. Top diagram, The general approach of Cre recombinase-dependent expression; Cre recombinase excises a stop cassette after the CAG promoter to enable hVOS probe transcription (probe expression is enhanced by the downstream woodchuck hepatitis virus post-transcriptional regulatory element) (Madisen et al., 2010, 2012). A–F, Probe fluorescence in brain sections from mice obtained by crossing Ai35-hVOS mice with various Cre drivers. A, hVOS::Parv double-transgenic mice express probe in layers 2/3 and 5 of the somatosensory cortex. White arrowheads indicate probe-expressing cells. B, hVOS::CalCrl mice express probe in hilar mossy cells of the DG (top) and in interneurons of layer 2/3 of the somatosensory cortex (bottom). C, hVOS::GAD2 mice express probe in the CA3 region of the hippocampus (top) and inner molecular layer of the DG (bottom). D, hVOS::Calb2 mice express probe in interneurons in layer 5 of the somatosensory cortex (top) and in a hilar mossy cell in the DG (bottom). The image was enhanced by GFP immunofluorescence to show the finer structure (thorny excrescences) of mossy cell dendrites. E, hVOS::Fos mice exposed to a novel environment express probe in neurons scattered through the granule cell layer of the DG. F, hVOS::Nestin mice express probe in newborn neurons in the granule cell layer of the DG.
