Figure 1.
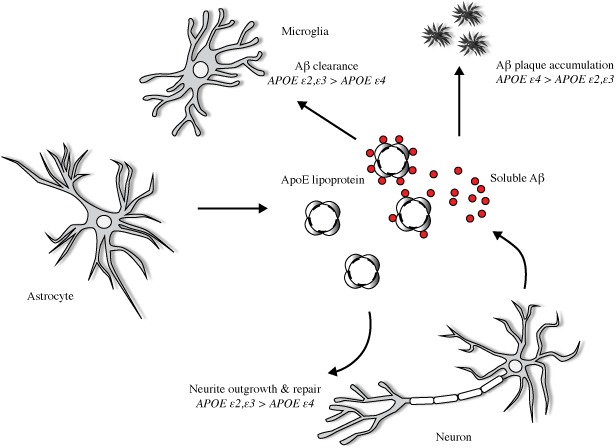
Effects of APOE on Aβ metabolism and postinjury repair. Neuronal injury upregulates astrocyte secretion of ApoE, which clears lipid cell debris and assists in cholesterol delivery for synaptogenesis. APOE is lipidated to form ApoE lipoprotein, and in the extracellular space binds in an isoform‐dependent pattern (APOE‐ε2, ‐ε3 > APOE‐ε4) to soluble beta‐amyloid protein (Aβ), a peptidic neurotoxin. APOE genotype determines the capacity for Aβ clearance and parenchymal amyloid plaque accumulation. Evidence suggests that relative to APOE‐ε2 and ‐ε3,APOE‐ε4 is preferentially susceptible to proteolytic degradation, thus reducing the capacity to fulfill postinjury needs for membrane repair and synaptogenesis
