Fig. 2.
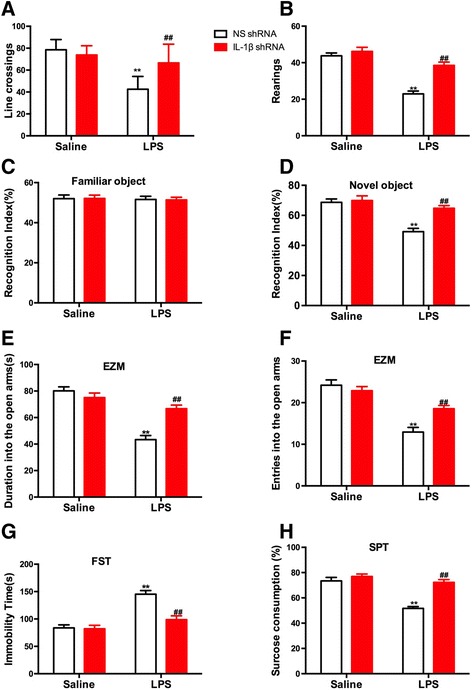
The influence of IL-1β knock-down in the DG regions of the hippocampus on locomotor activity and on anxiety- and depression-like behaviors induced by LPS in mice. Knock-down of IL-1β in the DG regions of the hippocampus alleviated the downregulation of locomotor activity induced by LPS, reflected by the line crossing (a) and rearing (b) in mice. c The recognition index had no significant difference for familiar objects among all the treatments in mice. d However, knock-down of IL-1β in the hippocampus alleviated the downregulation in the recognition index for novel objects induced by LPS in mice. The decrease e in duration in the open arms and f in entries into the open arms induced by LPS was blocked by pretreatment with the IL-1β shRNA lentivirus in the DG regions of the hippocampus of mice. g The increase in immobility time in the FST induced by LPS was significantly alleviated by pretreatment with the IL-1β shRNA lentivirus into the DG regions of the hippocampus of mice. h The decrease of sucrose consumption in the SPT induced by LPS was blocked by pretreatment with the IL-1β shRNA lentivirus into the DG regions of the hippocampus of mice. The data are expressed as the mean ± S.E.M (n = 16 per group). **p < 0.01 compared with the NS shRNA plus saline group; ##p < 0.01 compared with NS shRNA + LPS group
