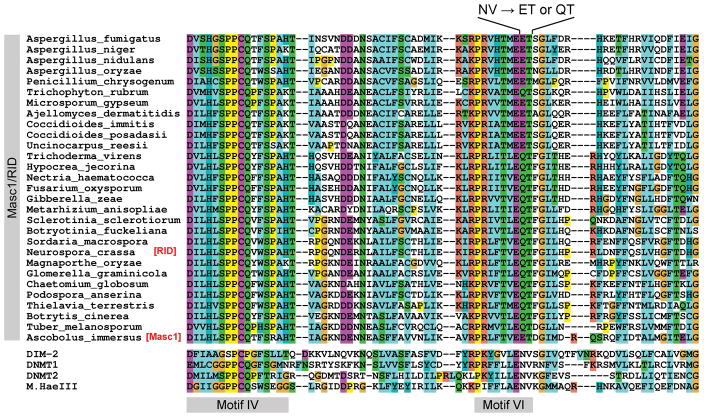
FIGURE 1.
The structure of Motif VI in Masc1/RID proteins is not canonical. The canonical Motif VI contains the absolutely conserved NV diad (asparagine-valine). This diad is present in all C5-cytosine methyltransferases except Masc1/RID. The asparagine residue of NV physically interacts with the proline residue of the catalytic triad PCQ (in Motif IV) and thus plays a critical role by controlling the positions of these segments with respect to one another in the native structure of the protein. The valine residue of NV is also functionally important, as its substitution for alanine is known to inactivate the catalytic activity of M.HhaI. Yet in all Masc1/RID proteins the NV diad is replaced with either QT (e.g., in Neurospora RID) or ET (e.g., in Ascobolus Masc1), hinting at the possibility that Masc1/RID proteins might have unique catalytic and/or substrate requirements.