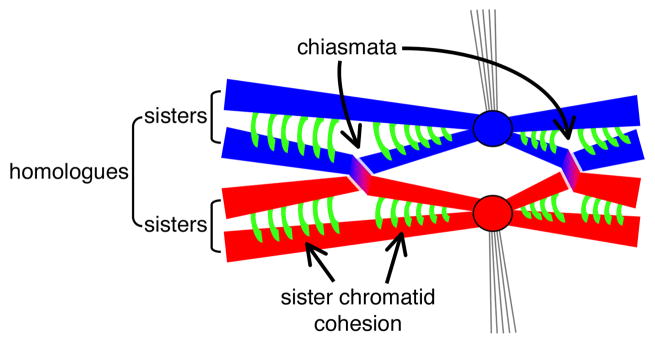
Figure 1. Connections formed between homologous chromosomes during meiosis.
Meiotic cells of most sexual organisms contain two copies of most chromosomes, one from each of the parents (red and blue). After DNA replication, each chromosome comprises a pair of sister chromatids held together by cohesion complexes (green). Sister centromeres (circles) attach as a single unit to microtubules (thin lines) from a spindle pole (not shown). Exchange of chromosome arms between non-sister chromatids yields a chiasma. Dissolution of sister chromatid cohesion along the arms allows the homologues to separate at the first meiotic division (not shown).