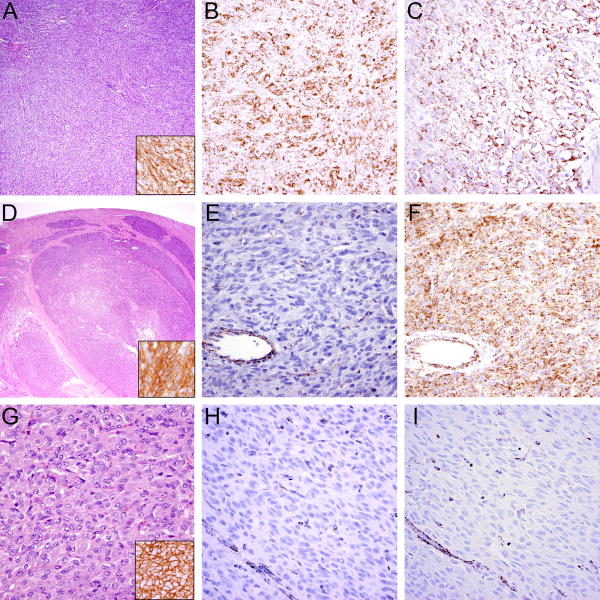
Figure 3.
Typical histologic features in GIST. A KIT-mutant GIST with sheet-like, solid growth (A) showing expression of DOG-1 (A, inset), SDHB (B), and SDHA (C). In contrast, SDH-deficient GISTs exhibit characteristic multinodular growth pattern at low power (D), are positive for DOG-1 (D, inset) and lack SDHB expression (E). In this case, SDHA expression (F) is retained, indicating the GIST arises from mutation of SDHB, SDHC or SDHD, rather than SDHA. Another example of an SDH-deficient GIST showing the characteristic epithelioid morphology (G) and expression of DOG-1 (G, inset) with SDHB (H) and SDHA (I) loss of expression indicating an underlying SDHA mutation; vessels (bottom left) serve as positive internal control.