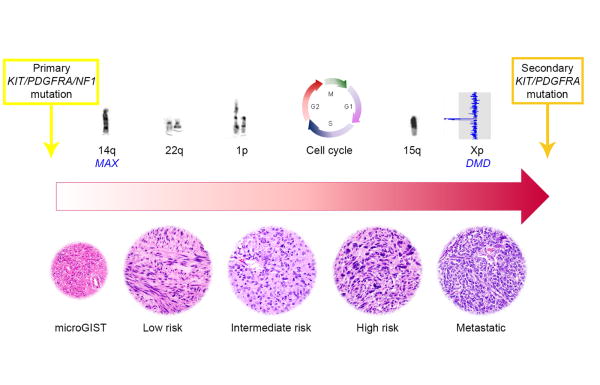
Figure 4.
Model of GIST genomic progression. Primary KIT, PDGFRA or NF1 mutations represent the initiating oncogenic driver events in most GISTs and are followed by stepwise accumulation of chromosomal aberrations, harboring putative tumor suppressor genes, and cell cycle dysregulating events. Metastatic GISTs develop treatment resistance through evolving TKI-resistant subclones with additional secondary KIT or PDGFRA mutations.