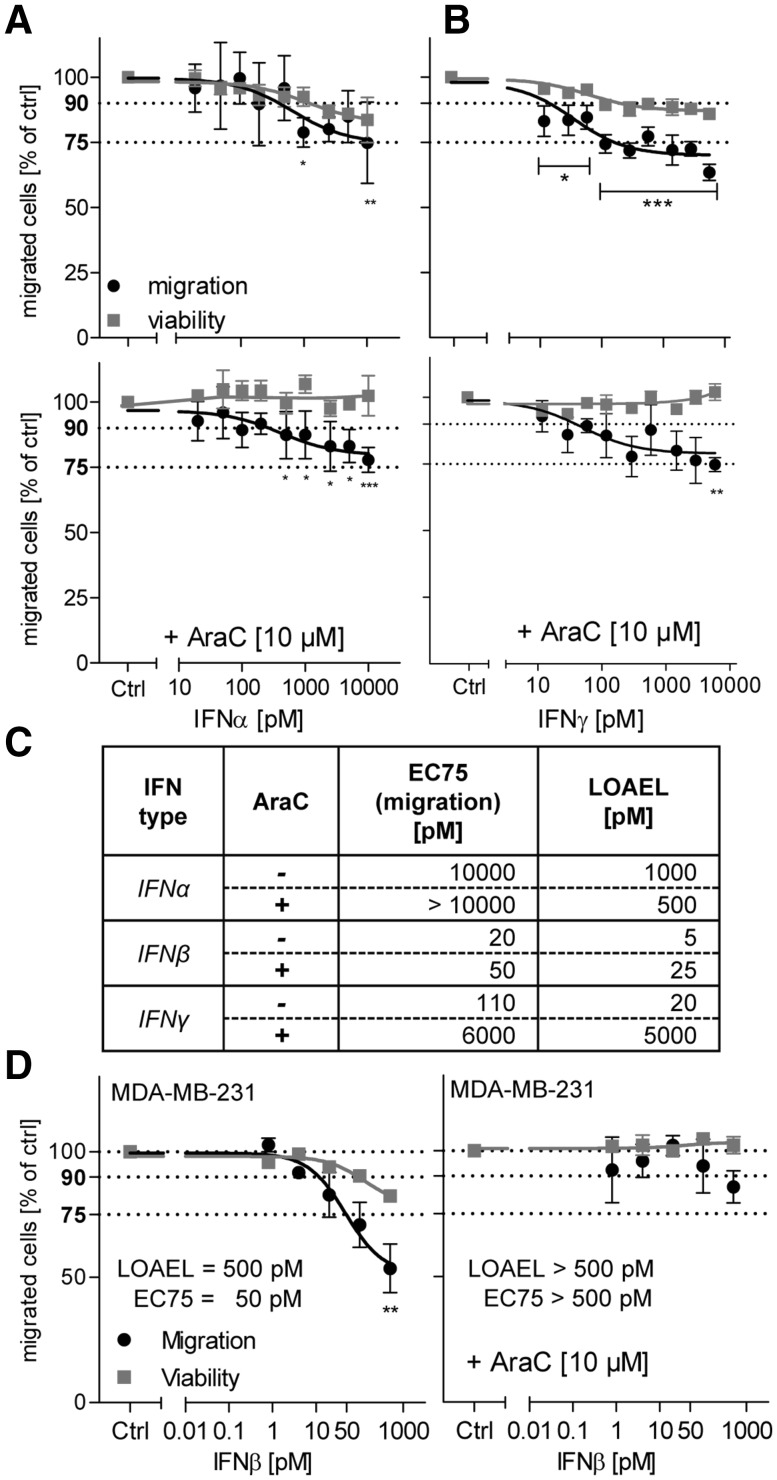
Fig. 2.
Specificity of IFNβ effects on NCC. NCC were treated for 48 h with interferons, while they were allowed to migrate. Then, the viability and the inhibition of cell migration were measured. All assays were performed either with or without cytosine arabinoside (AraC, 10 µM) as culture medium supplement. a, b Testing of interferon-α (IFNα) and interferon-γ (IFNγ). Data are from three independent experiments. Error bars indicate standard deviations (SD). Statistics was performed for each endpoint by ANOVA, followed by Dunnet’s post-hoc test (*p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001). c EC75 and the lowest observed adverse effect level (LOAEL) were compiled for each scenario. The LOAEL was defined as the lowest concentration triggering a significant reduction of cell migration (p ≤ 0.05). d Human breast cancer cells MDA-MD-231 were allowed to migrate for 48 h, before viability and the number of migrated cells were quantified. Cells were treated with the indicated concentrations of IFNβ for the total migration period, either with or without cytosine arabinoside (AraC, 10 µM) as culture medium supplement