Fig. 3.
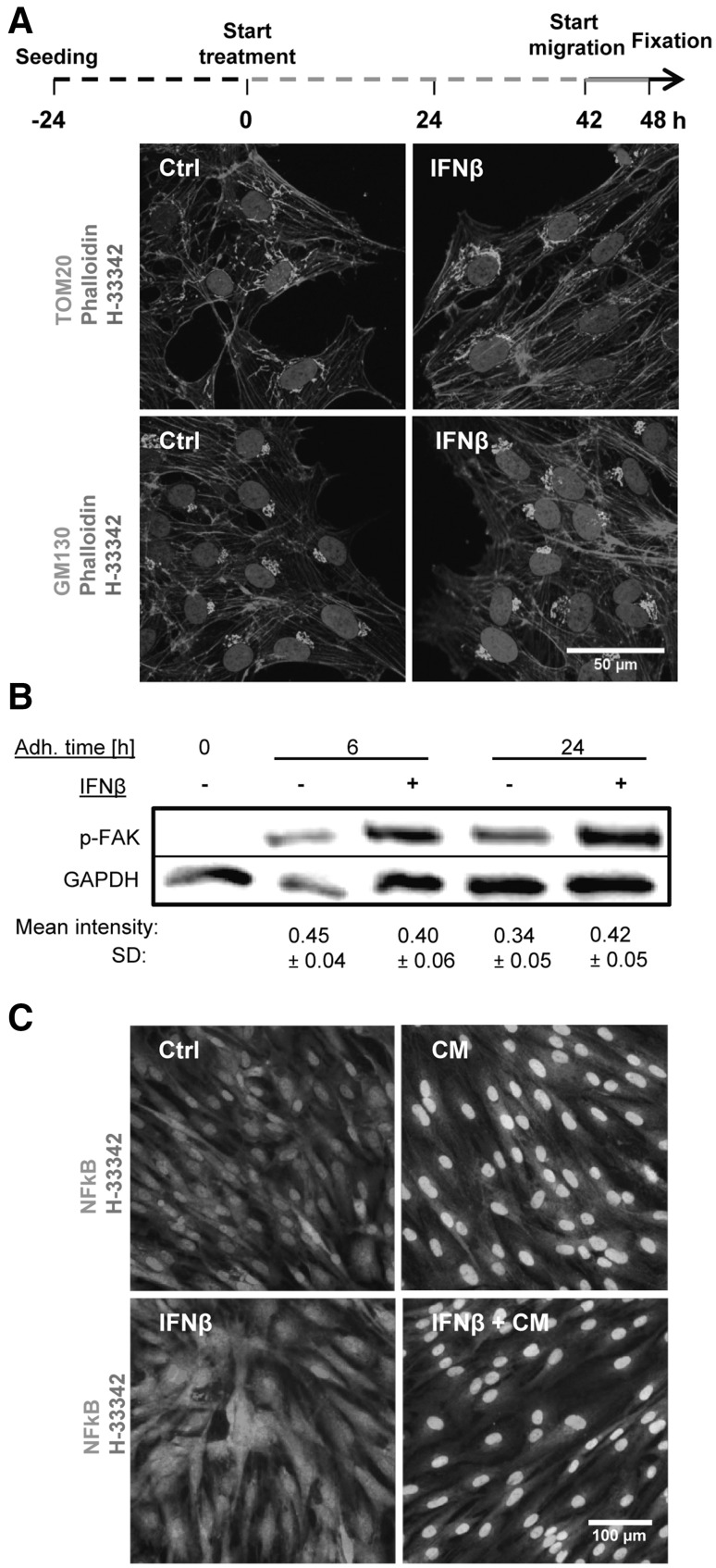
Maintenance of basic NCC functions and morphology in the presence of IFNβ. a NCC were treated with IFNβ (500 pM) or solvent (Ctrl) for 48 h, allowed to migrate in the last 6 h of the treatment period, and finally fixed for immunofluorescence staining. The microfilament cytoskeleton was visualized by phalloidin; antibodies to TOM20 were used to visualize mitochondria and anti-GM130 for the Golgi apparatus. b NCC were seeded for 0, 6, and 24 h (adhesion time) in culture medium supplemented with IFNβ (500 pM) or solvent. Then, cells were lysed and the amount of phosphorylated FAK was measured by Western blot analysis. The mean intensity of each band normalized to the respective loading control (GAPDH) ± SD is reported below each condition (n = 3). In the control (0 h = non-adherent cells), no band was detected. No significant change was observed between control and treatments at 6 and 24 h. c NCC were exposed to a cytokine mix (CM, 10 ng/ml TNFα, and 10 ng/ml IL1β), IFNβ (500 pM) or a combination of both for 1 h. Cells were then fixed and stained for nuclear factor kB (NFkB, green). Representative pictures for each condition are shown, with nuclei counterstained with H-33342 (red). Nuclei with translocated NFkB appear yellow, instead of red (non-translocated NFkB). (Color figure online)