Fig. 2.
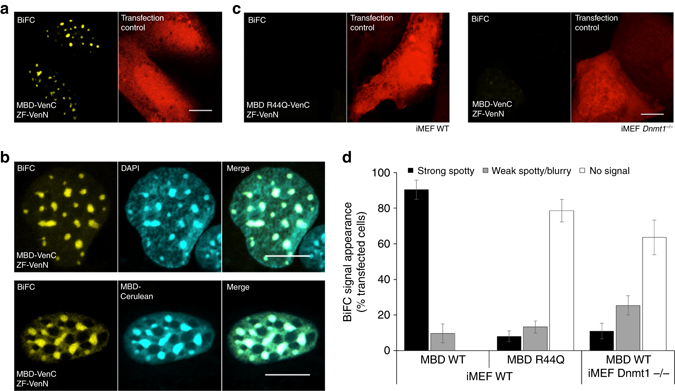
Development and validation of the BiAD sensor 1. a Representative fluorescence microscopy image of the BiFC signal (yellow channel) generated upon transfection of the BiAD sensor 1 in iMEF cells. A plasmid encoding NLS-mRuby2 was used to identify transfected cells (red channel). b Representative fluorescence microscopy images documenting co-localization of the BiFC signal with DAPI stained major satellite DNA (upper panel) and 5mC marks detected by co-transfection of the sensor modules with MBD-Cerulean (lower panel). c Representative fluorescence microscopy images documenting the 5mC specificity of the BiAD sensor. The BiFC signal was lost with the MBD R44Q 5mC-binding pocket mutant (left) and in cells with globally reduced DNA methylation levels (right). A plasmid encoding NLS-mRuby2 was used to identify transfected cells (red channel). The transfection, imaging and display settings of the images shown in panels a, c are identical. d Quantification of the experiments representatively shown in panels a–c. The error bars represent the s.e.m. for two biological repeats (for details cf. Methods and Supplementary Tables 1, 6, and 7). All cells were fixed at 48 h after transfection. Scale bar for all images is 10 µm
