Table 2. Solid phase synthesis of HGF K1 domains using AcAO linker.

| |||||
| Entry | Polypeptide b | Peptide (# of AA) | Cleavage method c | % +16 u by-product d | % Yield (average yield per step) e |
| 1 |
CIIGKGRSYKGTVSITKSGI QPWSSMIPHEHSFLPSSYRGKDLQEN QPWSSMIPHEHSFLPSSYRGKDLQEN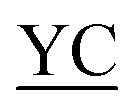 RNPRGEEGGPWCFTSNPEVRYEVCDIPQCSEVK(biotin)-NH2 RNPRGEEGGPWCFTSNPEVRYEVCDIPQCSEVK(biotin)-NH2
|
17 (83) | A | 40 | 28 (81) |
| 2 |
AIR IIGKGRSYKGTVSITKSGI IIGKGRSYKGTVSITKSGI QPWSSMIPHEHSFLPSSYRGKDLQEN QPWSSMIPHEHSFLPSSYRGKDLQEN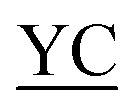 RNPRGEEGGPWCFTSNPEVRYEVCDIPQCSEV-NH2 RNPRGEEGGPWCFTSNPEVRYEVCDIPQCSEV-NH2
|
18 (87) | A | 45 | 23 (83) |
| 3 | See entry 1 | 17 (83) | B | < Detection limit | 21 (73) |
aElongation cycle: (1) SEAoff → MPA thioester: 6 M Gn·HCl, TCEP, 5% vol HSCH2CH2CO2H, pH 4.0, 37 °C, 24 h; (2) NCL: 6 M Gn·HCl, MPAA, pH 7.2, 37 °C, 24 h (see ref. 25).
bThe formed junctions are underlined. The residue modified by the AcA group is indicated in bold.
cMethod A: 20% AcOH, 0.1 M H2NOH and 1 M aniline, pH 4.3, 45 °C. Method B: 20% AcOH, 0.025 M H2NOH and 3 M aniline, pH 3.0, 45 °C.
dThe proportion of the by-product was estimated by high resolution ESI MS.
eOverall yield starting from AcA segment 1. Isolated by HPLC.
