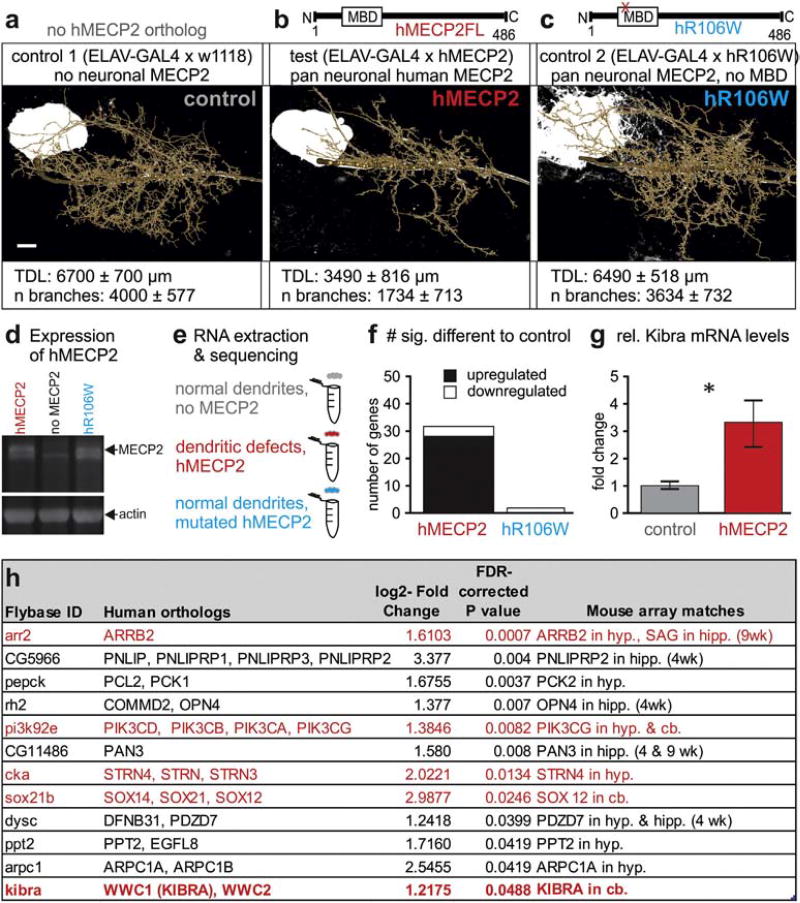
Fig. 1.
Expression of hMECP2 in Drosophila CNS causes MBD dependent changes in gene expression. a–c. Previously reported dendritic phenotypes with targeted hMECP2 expression in the identified Drosophila motoneuron, MN5. Statistically significant reductions in total dendritic length are caused by targeted expression of hMECP2 (b), but not with targeted expression of hMECP2 with a point mutated non-functional MBD, hR106W (c). d. Western blot reveals similar expression levels MECP2 following pan neuronal expression of hMECP2 (left lane) or of hR106W (right lane). The specific MECP2 band (see upper black arrow) is absent from controls (middle lane). Actin was used as loading control (lower black arrow). e. Schematic of RNA-Seq study design following no expression of hMECP2 and pan-neuronal expression of either hMECP2 or hR106W. f. Histogram comparing gene expression differences identified by RNA-Seq. g. qRT-PCR validation of dkibra upregulation with hMECP2 expression (n= 7) versus control (n= 8) (p < 0.05, t13 = 2.56, Welch's corrected two-tailed t-test). h. List of top twelve candidate genes from RNA-Seq. Genes interacting with the Hippo signaling pathway are identified by red text. Hyp.= hypothalamus, cb. = cerebellum, hipp. = hippocampus. Scale bars represent 10 µm.