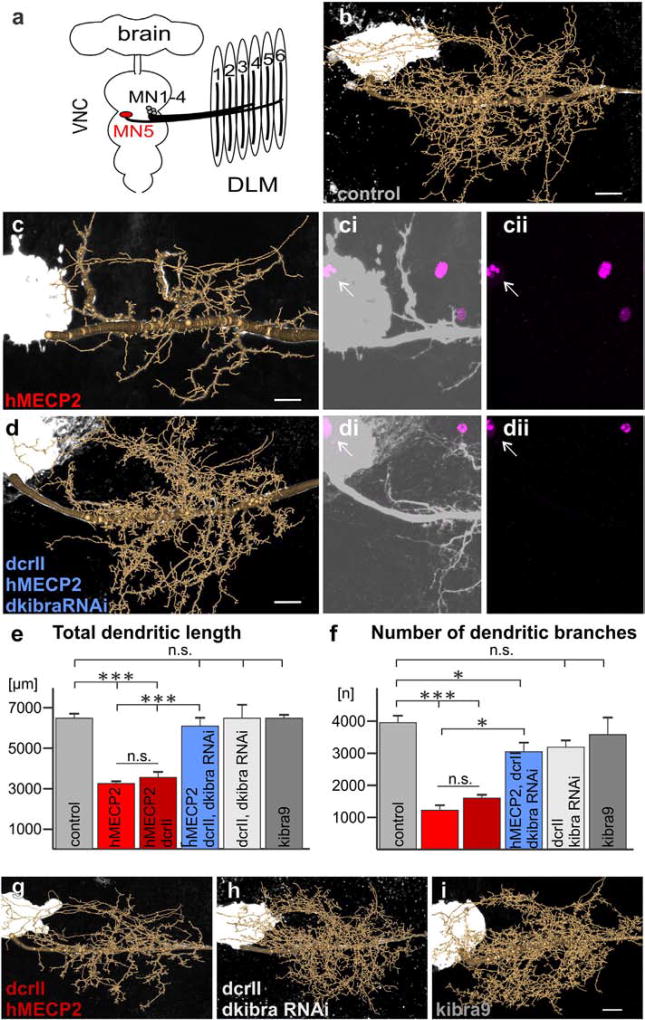
Fig. 3.
induced dendritic defects in Drosophila MN5. a. Schematic of Drosophila CNS and dorsal longitudinal flight depressor muscle innervation by MNs 1–5. b–d, g–i. Representative geometric reconstructions of MN5 dendritic trees superimposed onto representative projection views for each labeled group. ci–ii, di–ii. hMECP2 (magenta) is expressed and localizes to the nucleus of MN5 (white arrows) with (di–ii) and without (ci–ii) knockdown of dkibra. e,f. Quantification of total dendritic length (e) and number of branches (f) for all experimental and control genotypes (***p < 0.0001, *p < 0.05 Tukey post-hoc following two-way ANOVA, F5,46 = 56.30, p < 0.0001, n = 3–7 cells per group). All constructs were expressed using the C380-GAL4, cha-GAL80 driver line (see Online Methods for complete list of genotypes). Scale bars represent 10 µm.