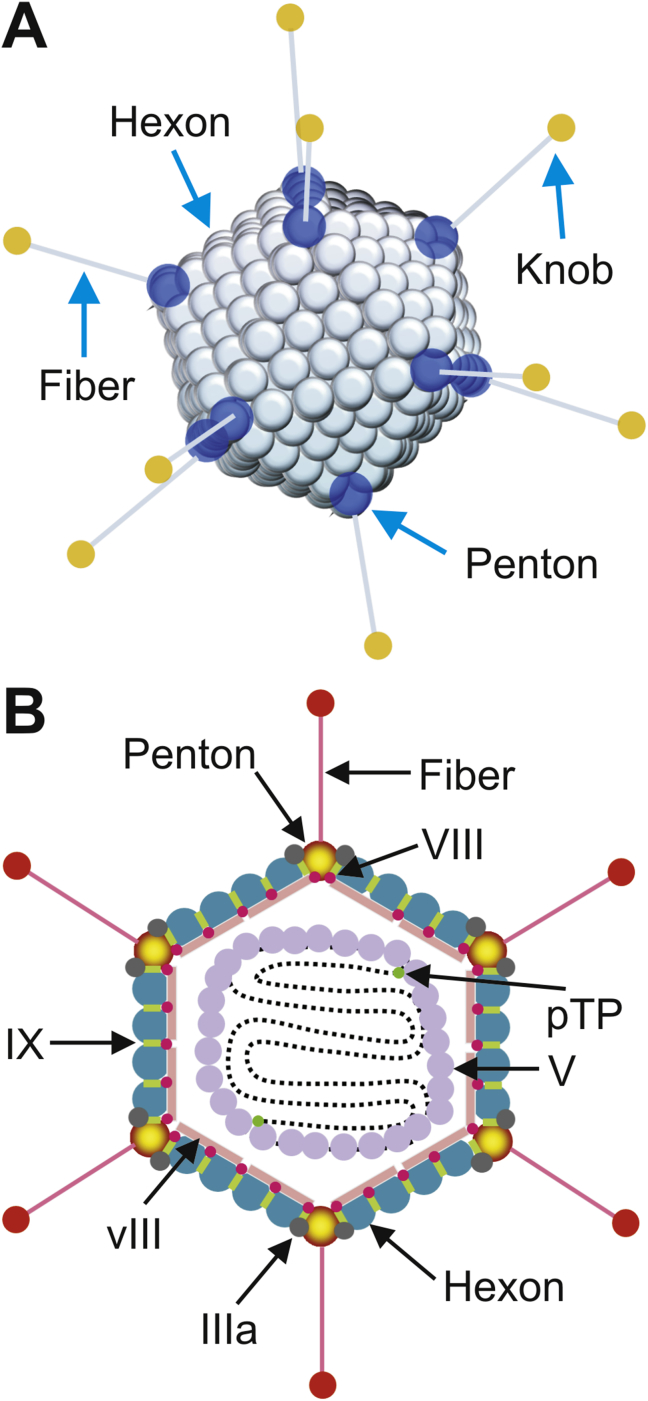
Figure 2.
The structure of adenovirus. (A) Adenovirus is a large, non-enveloped virus presenting icosahedral symmetry. The hexon, penton base, and knobbed fiber, are the most important capsid proteins for gene delivery. (B) Hexon is the major protein forming the 20 triangular faces of the viral capsid. The 240 hexon capsomers in the capsid are trimers, each interacting with six other trimers. The 12 vertices are formed by the penton capsomere, a complex of five copies of the penton base, and three copies of fiber. Each penton capsomere interacts with five hexon capsomeres, one from each of the five faces that converge at the vertex. The knobbed fiber protrudes from the fiber base. In addition, the 5′ termini of adenovirus genome bind covalently to the precursor terminal protein (pTP). The viral genome DNA is wrapped in a histone-like protein and contains the inverted terminal repeats (ITRs), which act as origins of replication.