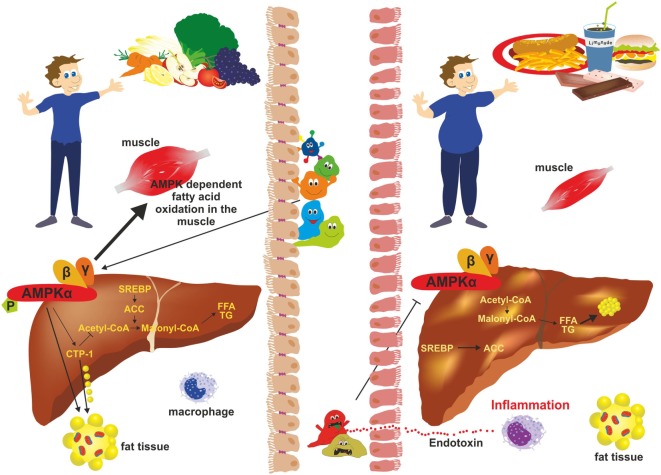
Figure 6.
Adenosine monophosphate kinase (AMPK) activity and gut microbiota. In subjects with a balanced “good” microbiota (left), AMPK phosphorylates key regulatory factors [e.g., acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1 (ACC1); sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1c (SREB1c)] that inhibit synthesis of fatty acids, cholesterol, and triglycerides. It further stimulates β-oxidation and glucose uptake in skeletal muscle and inhibits gluconeogenesis in the liver. During dysbiosis (right), “bad” gut microbiota inhibits phosphorylation of AMPK thereby negatively influencing hepatic fatty oxidation and favoring lipogenesis resulting in excessive fat storage in the liver and obesity.