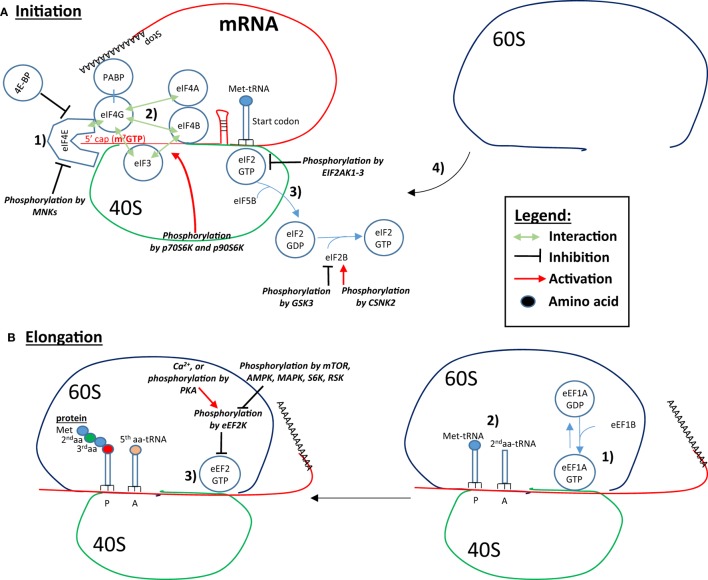
Figure 2.
Controls of initiation and elongation of protein translation. (A) Initiation: (1) eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E (eIF4E) binds to the 5′-cap structure of the mRNA and eIF4G, which interacts with eIF4A and eIF4B. eIF4G also interacts with the poly-A binding protein (PABP), which circularizes the mRNA and increases the translation rate. (2) eIF4B and eIF4G binds to eIF3, which is associated with the ribosomal 40S subunit, which forms the link between the mRNA, the ribosome and the complex eIF2-GTP/Met-tRNA. In addition, the initiation factors/40S complex scan the 5′UTR until the recognition of the start codon. (3) Protein translation is initiated by the eIF5B-catalyzed eIF2-GTP hydrolysis into GDP, which results in the freeing of the ribosomal 40S from eIF2 and other initiation factors. (4) The recruitment of the 60S ribosomal subunit forms the ribosome by binding to the 40S subunit. eIF4B interaction with eIF3 is increased by p70S6K- and p90S6K-mediated phosphorylation. Binding of eIF4E to eIF4G and to the 5′ cap can be inhibited by 4E-BP and by Mnk-mediated phosphorylation. Phosphorylation of eIF2 by the EIF2AKs inhibits eIF2 recycling. eIF2B is phosphorylated and inhibited by glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK3), while phosphorylation of eIF2B by CSNK2 increases its activity toward eIF2 recycling. (B) Elongation: (1) eEF1A-GTP recruits the second aminoacyl (aa)-tRNA on the A-site. (2) A peptide bond forms between Met and the second aa. (3) eEF2-GTP pushes the mRNA, Met-tRNA is removed from the P-site and is replaced by the next aa-tRNA previously on the A-site. In addition, a third aa-tRNA is placed in the now empty A-site. Eukaryotic elongation factor 2 (eEF2) is inhibited by eEF2K-mediated phosphorylation. EEF2K is inhibited by mTOR, AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), S6K, and RSK. Conversely, Ca2+ and PKA phosphorylation leads to eEF2K phosphorylation and activation, and inhibition of the elongation.