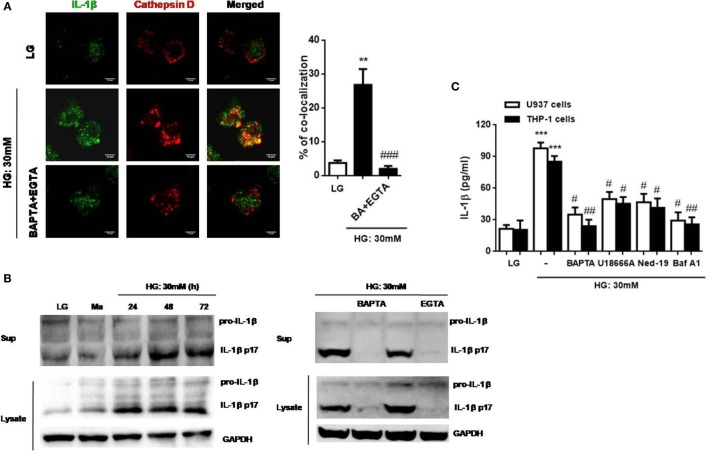
Figure 5.
High glucose (HG) induced cathepsin d-dependent interleukin-1β (IL-1β) secretion, which was dependent on lysosomal Ca2+ release in U937 and THP-1 cells. (A) Immunofluorescence images showing the location of IL-1β and cathepsin D in fixed U937 cells under HG (30 mM glucose for 48 h) by confocal microscopy. The U937 cells were pre-treated with BAPTA (10 µM) plus ethylene glycol tetra acetic acid (EGTA) (5 mM). The percentages of co-localization were calculated as the average volume of the overlapping areas (n = 4). (B) Representative immunoblots for pro-IL-1β, IL-1β (p17), and GAPDH protein expressions under low glucose (LG; 5.5 mM glucose for 48 h) or HG (30 mM glucose for 24–72 h), or in the presence of BAPTA (BA; 10 µM) or EGTA (5 mM) under HG (30 mM glucose for 48 h) in U937 cells. (C) ELISA for IL-1β secretion from the supernatants of treated cells. U937 cells were stimulated with HG (30 mM glucose for 48 h) in the presence of BAPTA (10 µM), or with the pre-treatment of U18666A (2 µg/ml), trans-Ned-19 (Ned-19; 100 µM), or bafilomycin A1 (Baf A1; 500 nM). Data were shown as mean ± SEM. (A,C) **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001 vs. LG; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, and ###P < 0.001 vs. HG.