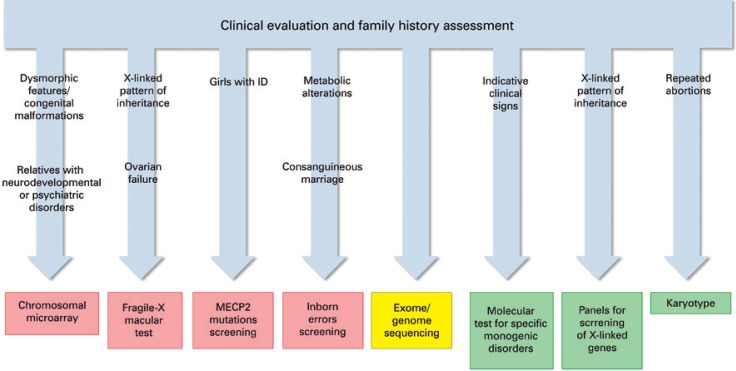
Figure 2. Genetic counseling in autism spectrum disorder.
The first important step in genetic counseling is the clinical evaluation of the patient and the assessment of family history. This can provide valuable information that can direct molecular test to a more appropriated choice. As a general rule, chromosomal microarray, fragile X test for males, MECP2 mutation screening for females and inborn errors screening should be performed for all patients diagnosed with ASD (red). Particular situations can direct the choice specifically to one of these tools. As a second-tier diagnostic tool, exome or genome sequencing can be applied (yellow). Characteristic clinical signs, pattern of inheritance or history of repeated abortions can be indicative of specific genetic alterations that can be screened with more specific molecular tools (green).