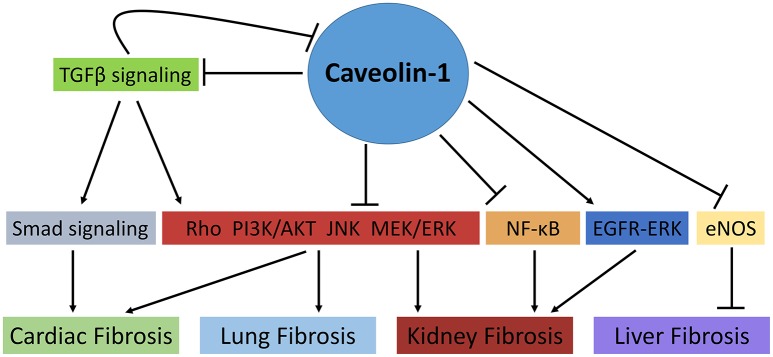
Figure 1.
The role of Caveolin-1 in cellular signaling mechanisms involved in fibrosis. Caveolin-1 (Cav-1) directly and indirectly regulates fibrotic processes in various tissues. In cardiac and lung fibrosis, Cav-1 prevents collagen deposition, fibroblast proliferation and TGFβ signaling through its negative regulation of Smad and non-Smad signaling pathways such as Rho-like GTPase, PI3K/AKT, MAPK (MEK/ERK), and JNK signaling pathways. Similarly, in kidney fibrosis, Cav-1 modulates fibrotic processes via the aforementioned pathways as well as NF-κB signaling. Of note, TGFβ signaling can also mediate Cav-1 expression via the activation of non-SMAD signaling pathways. Conversely, Cav-1 has been shown to promote kidney fibrosis by prolonging EGFR-ERK signaling. Moreover, in liver fibrosis, Cav-1 promotes liver cirrhosis through its negative regulation of eNOS ( , activation;
, activation;  , inhibition).
, inhibition).