Fig. 2.
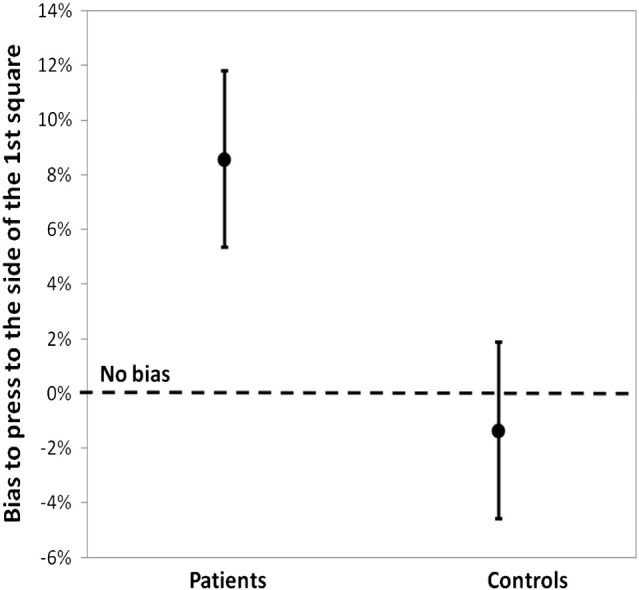
Amplitude of the bias (in %) to the side of the 1st or 2nd stimulus, when one stimulus is displayed on the right side of the screen and the other one on the left. A positive bias corresponds to a bias to the side of the first stimulus (in patients), whereas a negative bias corresponds to a bias to the side of the second stimulus (in healthy participants). See Lalanne et al. (2012a) and (2012b), for more detailed results.
