Figure 1. TFEB inhibits cross-presentation in DCs.
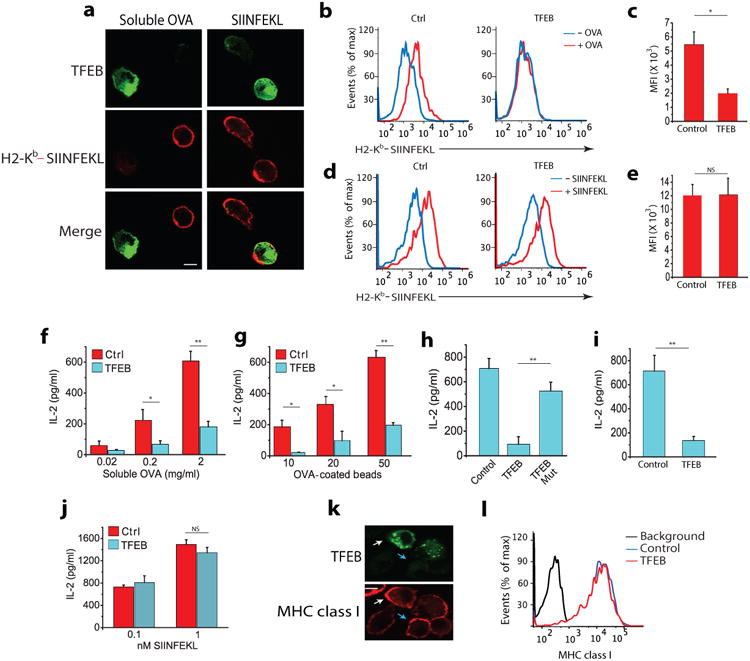
(a) Immunofluorescence of surface expression of Kb-SIINFEKL complexes in non-permeabilized BMDCs transduced with TFEB-EGFP assessed by staining with mAB 25.D1 following incubation with 2mg/ml soluble OVA or 2nM free SIINFEKL peptide for 3 hours. (b-e) Flow cytometry analysis of Kb-SIINFEKL complex expression on the surface of BMDCs transduced with TFEB-EGFP or control-EGFP vectors after they were incubated with OVA protein or free SIINFEKL peptide. (f,g) Cross-presentation-dependent T cell stimulation in response to TFEB-EGFP and control-EGFP transduced BMDCs incubated with soluble OVA or 3μm OVA-coated beads. The level of cross-presentation was determined by measuring the amount of IL-2 produced by B3Z cells by ELISA (h) Cross-presentation-dependent T cell stimulation in response to TFEB or nucleus translocation defective mutant TFEBMut-transduced BMDCs incubated with OVA. (i) TFEB-mediated cross-presentation of a viral epitope; TFEB transduced BMDCs were incubated with inactivated HSV-1 for 5 hours, fixed and co-cultured with T cells isolated from the spleen of gBT mouse. (j) Presentation of SIINFEKL peptide by TFEB-transduced and control BMDCs. (k,j) MHC class I (Kb) surface expression on BMDCs transduced with TFEB, evaluated on non-permeabilized cells by confocal microscopy (k) and flow cytometry (j). For all panels the data represents the mean ± SE from at least three independent experiments (cells isolated from at least three different mice) unless otherwise indicated. *P < 0.05 (Student's t-test).
