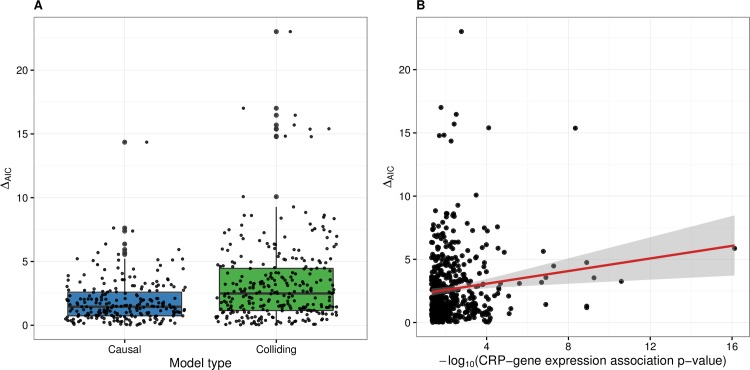
Fig 2. Analysis of ΔAIC values.
(A) Differences in the Akaike information criterion values between the causal and colliding models (ΔAIC) in triplets best supported by either model. On average, the colliding models have higher ΔAIC values. This indicates that we are more likely to identify genes whose expression is in some way regulated by CRP. (B) Scatter plot of ΔAIC values against the CRP-expression association p-values with a linear trend and 95% confidence interval. Despite a small positive trend, we can observe that higher correlation does not necessarily translate to more evidence of a causal effect.