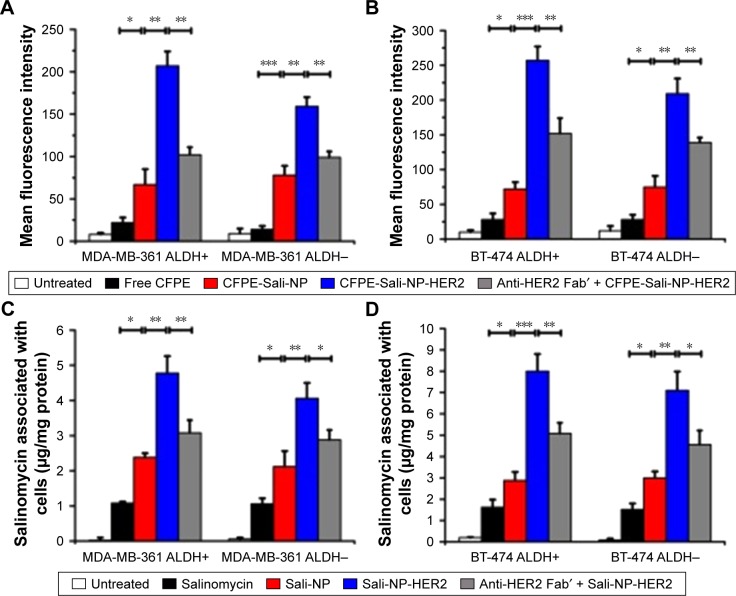
Figure 3.
In vitro cellular uptake of nanoparticles in breast cancer cells.
Notes: (A and B) In vitro cellular uptake of nanoparticles, evaluated by flow cytometry. Breast cancer cells were incubated with free CFPE, CFPE-Sali-NP, or CFPE-Sali-NP-HER2 for 4 h. In the competitive assay (CFPE-Sali-NP-HER2 + anti-HER2 Fab′), 50 mg/mL of anti-HER2 Fab′ was preincubated with the cells for 30 min prior to treatment with CFPE-Sali-NP-HER2. (C and D) In vitro cellular uptake of nanoparticles, evaluated by HPLC. Breast cancer cells were incubated with free salinomycin, Sali-NP, or Sali-NP-HER2 at a concentration of 50 μg/mL salinomycin for 4 h. In the competitive assay (Sali-NP-HER2 + anti-HER2 Fab′), 50 mg/mL of anti-HER2 Fab′ was preincubated with the cells for 30 min prior to treatment with Sali-NP-HER2. The intracellular uptake of salinomycin was calculated as intracellular salinomycin mass divided by cellular protein mass. Differences between groups were compared by one-way ANOVA and the Newman–Keuls method. Data are expressed as mean ± SD (n=3). *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001.
Abbreviations: ANOVA, analysis of variance; CFPE, 1,2-dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine-N-carboxyfluorescein (ammonium salt); CFPE-Sali-NP, CFPE-labeled salinomycin-loaded polymer–lipid nanoparticles; CFPE-Sali-NP-HER2, CFPE-labeled salinomycin-loaded polymer–lipid anti-HER2 nanoparticles; HPLC, high-performance liquid chromatography; Sali-NP, salinomycin-loaded polymer–lipid nanoparticles; Sali-NP-HER2, salinomycin-loaded polymer–lipid hybrid anti-HER2 nanoparticles.