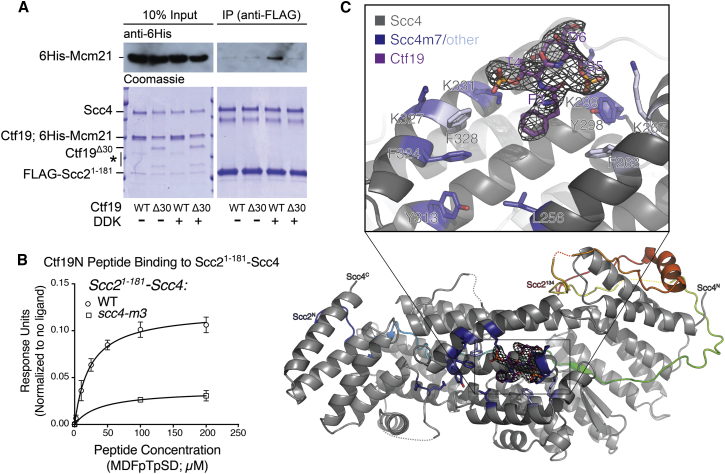
Figure 6.
Scc4 Recognizes Phosphorylated Ctf19
(A) Reconstitution of DDK-dependent Scc4-Ctf19 interaction in vitro. Recombinant Ctf19-6His-Mcm21 complexes were phosphorylated with purified DDK and then used for pulldowns with recombinant FLAG-Scc21–181-Scc4. Proteins were immunopurified on anti-FLAG beads, resolved by SDS-PAGE, and detected by immunoblot against an 6His-Mcm21 (top) or by Coomassie stain (total protein, bottom; ∗, degradation product).
(B) Synthetic Ctf191–6 peptide (MDFpTpSD) was tested for binding to Scc21–181-Scc4WT or Scc21–181-Scc4m3. Mean average scaled response units are shown for three independent experiments for each data point.
(C) Structure of phosphorylated Ctf191–6 bound to Scc21–181-Scc4. An overview of the complex (bottom) is shown as a cartoon with Scc4 in gray and Scc21-181 in rainbow (violet, N terminus; red, C terminus). The Ctf19-Scc4 interaction is shown in detail above. Individual residues mutated in the scc4-m7 allele are in purple. Other residues contributing to the interaction are in light blue. Ctf19 is purple with non-carbon atoms colored by element (red, oxygen; blue, nitrogen; yellow, phosphorous). Omit map density contoured to 0.8 sigma is shown for the Ctf19 peptide.